2025-08-27 中国科学院(CAS)
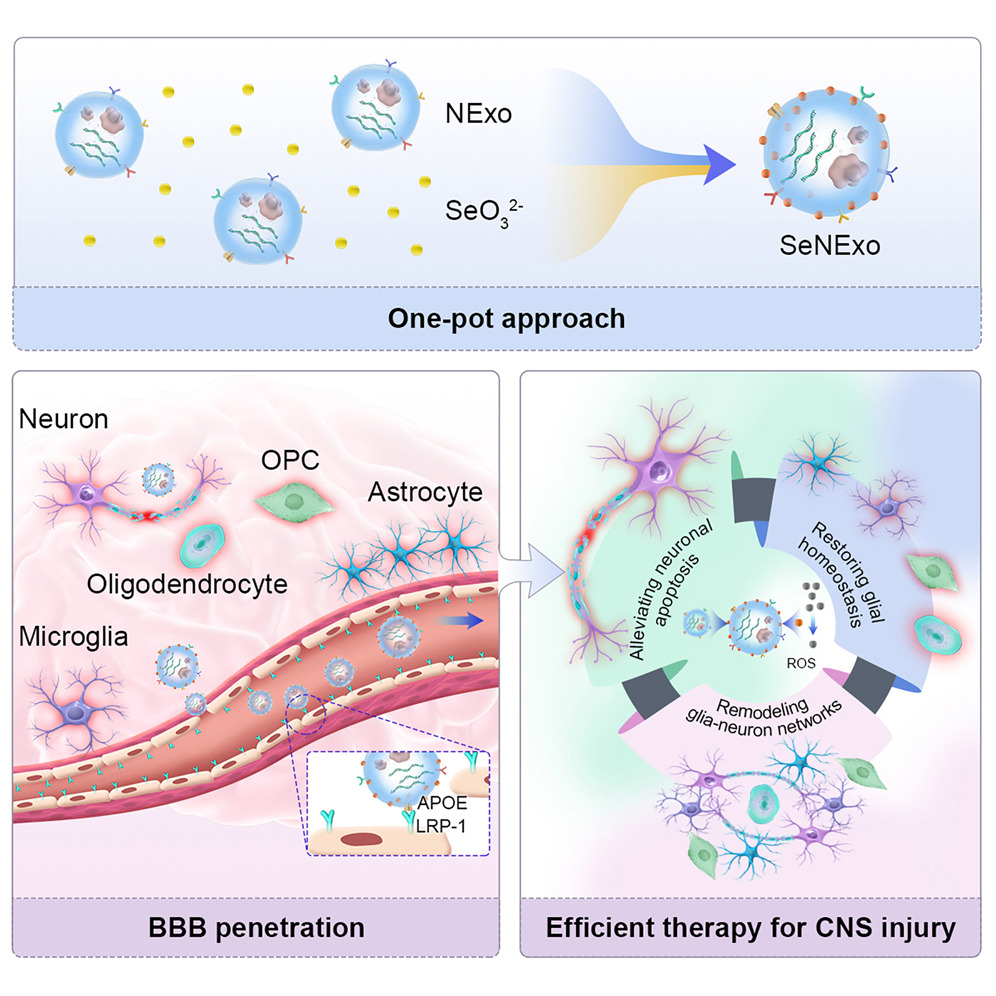
Schematic diagram of the preparation, blood-brain barrier penetration, and synergistic neural repair of SeNExo. (Image by WANG Wenjing)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/chem/202508/t20250820_1051108.shtml
- https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-medicine/fulltext/S2666-3791(25)00392-1
セレン化神経幹細胞由来エクソソーム:中枢神経系外傷性損傷に対する新種の治療剤 Selenized neural stem cell-derived exosomes: A neotype therapeutic agent for traumatic injuries of the central nervous system
Wenjing Wang ∙ Guihong Lu ∙ Peilin Guo ∙ … ∙ Hui Tan, ∙ Guanghui Ma ∙ Wei Wei
Cell Reports Medicine Published:August 28, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102319
Highlights
- NSC-derived exosomes are functionalized with ultrasmall nano-selenium
- SeNExo crosses the BBB by utilizing APOE_LRP-1 interaction
- SeNExo exhibits ROS scavenging and neuroprotection abilities
- Therapeutic efficacies are demonstrated in TBI and SCI model mice
Summary
Oxidative damage and neuroinflammation are the key features of central nervous system (CNS) injury. Inspired by the neuroprotective properties of neural stem cell-derived exosomes (NExo) and the reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging ability of selenium, we develop an advanced NExo bearing ultrasmall nano-selenium (∼3.5 nm) via lipid-mediated nucleation (SeNExo). In addition to maintaining the biological components of NExo, the resulting SeNExo exhibits a Se–O bond that dramatically enhances its ROS-scavenging performance. SeNExo penetrates the blood-brain barrier (BBB) via the apolipoprotein E and prolow-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (APOE_LRP-1) interaction. Through proteomics, microRNA (miRNA) omics, and single-nucleus RNA sequencing, we find that SeNExo can alleviate neuronal apoptosis, restore glia homeostasis, and remodel glia-neuron networks. Therefore, SeNExo confers potent therapeutic benefits, significantly reducing cerebral lesions in a murine traumatic brain injury model. Even extending to a murine spinal cord injury model, SeNExo promotes locomotory recovery, further supporting SeNExo as a neotype and a promising therapeutic agent for treating traumatic CNS injury.


