2025-10-14 テキサスA&M大学
Web要約 の発言:
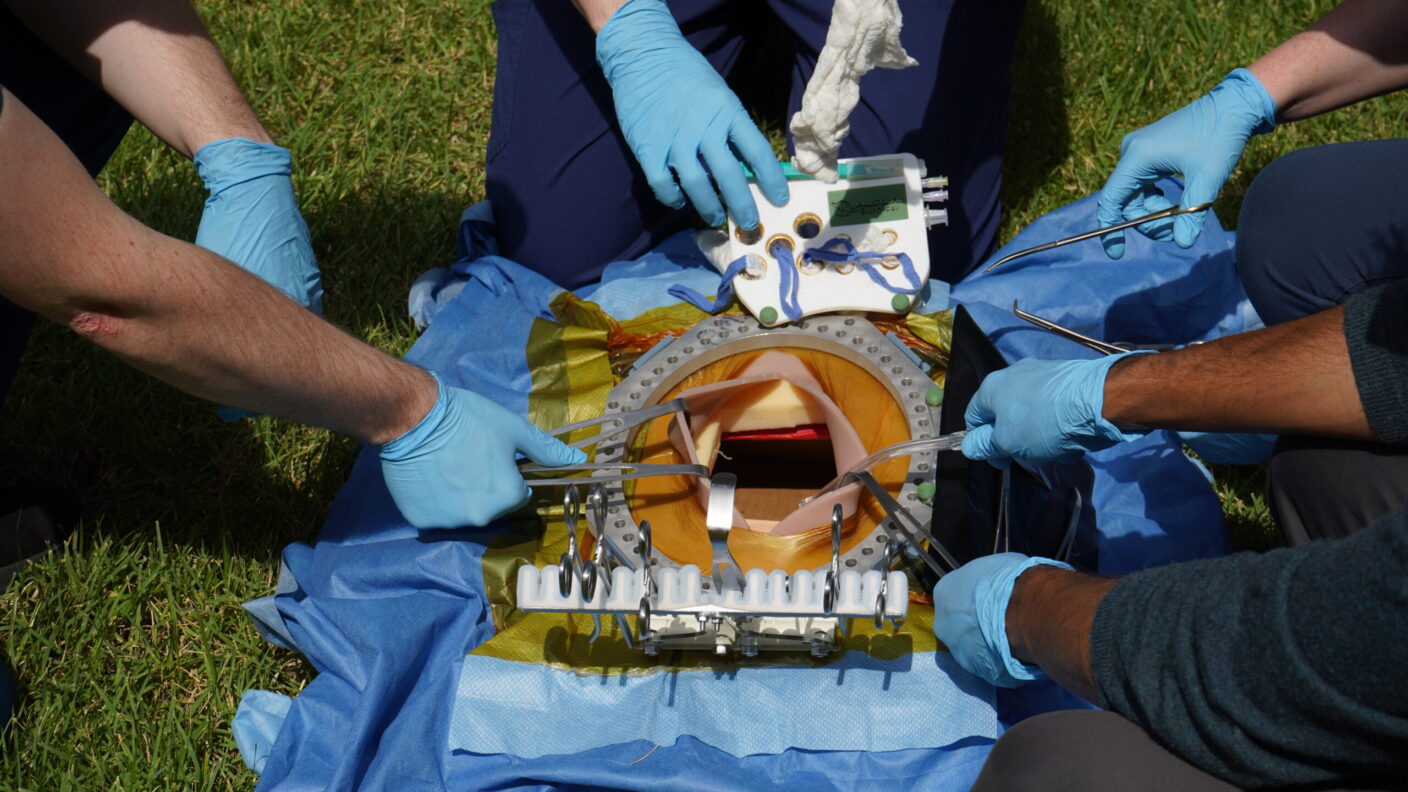
The WildOR Kit and ART system securely attach to the patient, creating a stable platform for deploying surgical tools and accessing the intervention site. Credit: Texas A&M University School of Engineering Medicine
<関連情報>
- https://stories.tamu.edu/news/2025/10/14/a-phone-book-sized-surgical-kit-designed-for-the-worlds-most-extreme-environments/
- https://www.annemergmed.com/article/S0196-0644(24)00775-3/abstract
322 汚れた道具できれいに切る:災害救助のための再利用可能な処置キットの開発 322 Clean Cuts With Dirty Tools: Developing a Reusable Procedure Kit for Disaster Relief
W. Hendricks ∙ N. Reid ∙ J. Paris ∙ B. Raper ∙ W. Cromer
Annals of Emergency Medicine
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2024.08.322
In disaster relief and humanitarian relief missions, the emergency physician’s role is critical in offsetting the surgical case volume by completing bedside procedures. A review of procedures in humanitarian relief missions over 4 years revealed common emergency department procedures as some of the most frequent cases: wound debridement, abscess drainage, and circumcision (12.1%); fasciotomy, and amputation of fingers or toes (9.2%); and drain insertion, chest tube insertion, and dressing changes (5.5%) were the 2nd, 4th, and 5th most common procedure categories. There exists a need for a versatile procedure kit with redundant methods for reusability in resource-limited settings. Given higher than typical surgical site infection rates in these environments, this study investigates different modalities of sanitization for the reuse of the proposed kit and traditional medical instruments when typical supplies begin to run low. While chlorhexidine (CHX) has been a standard for antiseptic treatment in hospitals, tablet-based sterilization methods such as tetraglycine hydroperiodide (Gly4I) and sodium dichloroisocyanurate (SDIC) have historical significance dating back to World War I, and their application extends to modern-day global health missions, military, and NASA operations. These methods are lightweight, compact, and already used in austere conditions to clean drinking water. This study assessed the efficacy of commonly carried water purification tablets (Gly4I and SDIC) as sanitizing agents for medical instruments, comparing them with conventional sanitization techniques.