2025-11-07 デューク大学(Duke)
<関連情報>
- https://pratt.duke.edu/news/congenital-heart-disease-kidney-damage/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-025-01543-0
人工多能性幹細胞モデルを用いた解析により、先天性心疾患に関連するSMAD2変異における有足細胞形成の変化が明らかになった Engineered human induced pluripotent stem cell models reveal altered podocytogenesis in congenital heart disease-associated SMAD2 mutations
Rohan Bhattacharya,Tarsha Ward,Titilola D. Kalejaiye,Alekshyander Mishra,Sophia M. Leeman,Hamidreza Arzaghi,Jonathan G. Seidman,Christine E. Seidman &Samira Musah
Nature Biomedical Engineering Published:03 November 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-025-01543-0
Abstract
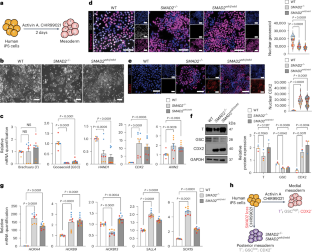
Clinical observations of patients with congenital heart disease carrying SMAD2 genetic variants revealed correlations with multi-organ impairments at the developmental and functional levels. Many patients with congenital heart disease present with glomerulosclerosis, periglomerular fibrosis and albuminuria. It remains largely unknown whether SMAD2 variants associated with congenital heart disease can directly alter kidney cell fate, tissue patterning and organ-level function. Here we investigate the role of pathogenic SMAD2 variants in podocytogenesis, nephrogenic cell lineage specification and glomerular filtration barrier function using a combination of CRISPR-based disease modelling, stem cell and microfluidic organ-on-a-chip technologies. We show that the abrogation of SMAD2 results in altered patterning of the mesoderm and intermediate mesoderm cell lineages, which give rise to nearly all kidney cell types. Following further differentiation of intermediate mesoderm cells, the mutant podocytes failed to develop arborizations and interdigitations. A reconstituted glomerulus-on-a-chip system showed substantial albumin leakage, as observed in glomerulopathies. This study implicates chronic heart disease-associated SMAD2 mutations in kidney tissue malformation that might inform targeted regenerative therapies.