2025-12-23 東京科学大学
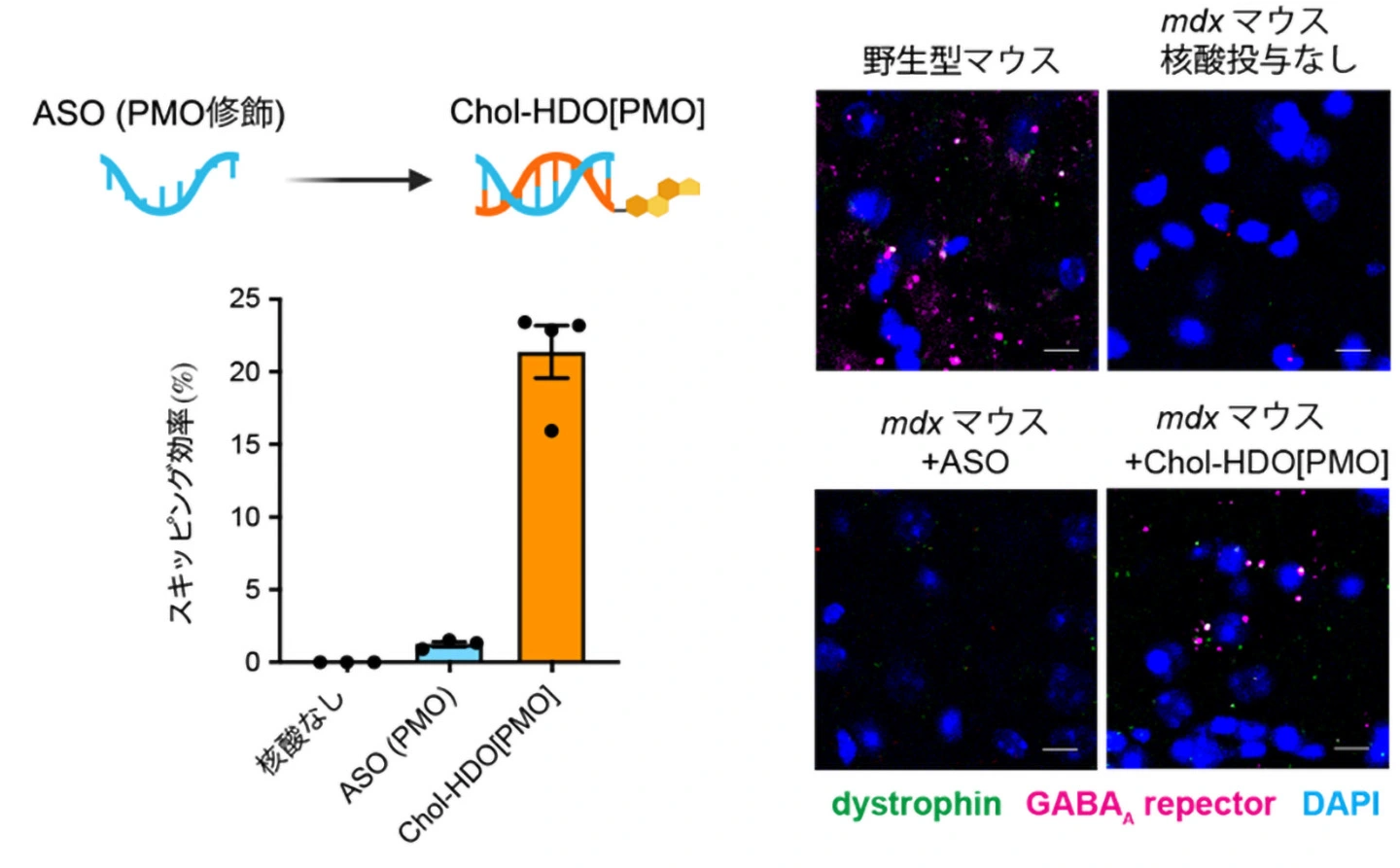
図1. 従来のASOとChol-HDO[PMO]の有効性の比較 (Created with BioRender.com)
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/1ejxd9qukbqx
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/1ejxd9qukbqx
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-66765-x
モルフォリノRNA二本鎖は、脳室内および脊髄腔内注射により、強力で持続的かつ安全な立体ブロックアンチセンス活性を示す Morpholino–RNA duplex exhibits robust, sustained, and safe steric-block antisense activity by intracerebroventricular and intrathecal injection
Mitsugu Yanagidaira,Tetsuya Nagata,Juri Hasegawa,Takashi Ishii,Satoe Ebihara,Makiko Nawa & Takanori Yokota
Nature Communications Published:22 December 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-66765-x
Abstract
Intrathecal injection of steric-block antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) provides therapeutic opportunities for targeting the central nervous system (CNS). Phosphorothioate backbone with 2′-O-methoxyethyl (MOE) is widely used in ASO drugs, with concerns about toxicity and potency. Phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer (PMO) is another chemistry with a favorable safety profile but less persistent effect due to its ineffective cellular uptake and poor binding affinity to serum proteins. Here, a cholesterol-conjugated PMO/RNA heteroduplex oligonucleotide (Chol-HDO[PMO]) outperformed conventional single-stranded ASOs, achieving up to a 16-fold increase in potency without detectable toxicity and maintaining stronger ASO activity throughout the observation period. Chol-HDO[PMO] showed enhanced antisense activity in both splice modulation and translation inhibition. Chol-HDO[PMO] successfully alleviated the CNS symptoms in a Duchenne muscular dystrophy mouse model. In contrast, Chol-HDO[MOE] failed to enhance tissue delivery or potency. The efficient tissue delivery relied on interactions with CSF lipoproteins, and binding affinity was determined by heteroduplex oligonucleotide chemistry. Collectively, Chol-HDO[PMO] may expand the therapeutic potential of steric-block ASOs targeting the CNS.


