2025-12-26 北海道大学
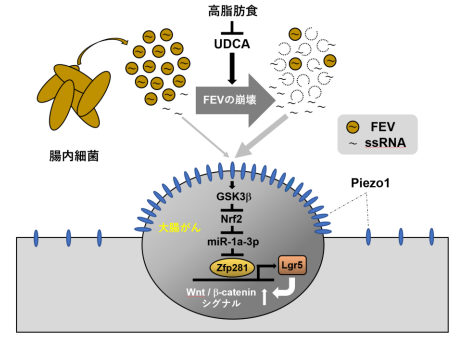
図 1 腸内細菌由来の RNA と機械刺激受容体 Piezo1 による大腸がん抑制機構
<関連情報>
- https://www.hokudai.ac.jp/news/pdf/251226_pr.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211124725015098
細菌由来の細胞分泌小胞に含まれる一本鎖 RNA は Peizo1 を介して大腸癌を抑制する Bacterial extracellular vesicle ssRNA prevents colorectal cancer progression via Piezo1
Takeshi Kondo, Yasunori Takayama, Yutaro Kumagai, Naoki Takemura, Shigetsugu Hatakeyama, Makoto Tominaga, Kenta Maruyama
Cell Reports Available online: 17 December 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116737
Highlights
- Fecal ssRNA originates from bacterial fecal extracellular vesicles (FEVs)
- UDCA gavage ruptures FEVs, increasing “naked” ssRNA and inhibiting CRC progression
- Fecal ssRNA suppresses colorectal cancer (CRC) proliferation via Piezo1
- ssRNA-Piezo1 axis suppresses Wnt/β-catenin signaling in CRC by inhibiting Zfp281
Summary
Single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) can activate the mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo1 in the gut. However, its source and role in colorectal cancer (CRC) remain unclear. In the present study, we demonstrate that ssRNA within fecal extracellular vesicles (FEVs) derived from bacteria, particularly those susceptible to lysis by ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), can suppress CRC progression via Piezo1 activation. Gut-specific Piezo1-knockout mice developed more tumors following CRC induction. Similarly, Piezo1-deficient CRC cell lines exhibited increased proliferation with upregulated Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mechanistically, Piezo1 activation downregulated the transcription factor Zfp281, decreasing the expression of its target gene Lgr5 and dampening Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Notably, oral UDCA administration enhanced FEV rupture, increasing luminal “naked” ssRNA and mitigating high-fat diet-induced CRC in vivo. These findings identify the bacterial ssRNA-Piezo1 axis as a potential therapeutic target in CRC.


