2026-01-13 東京科学大学
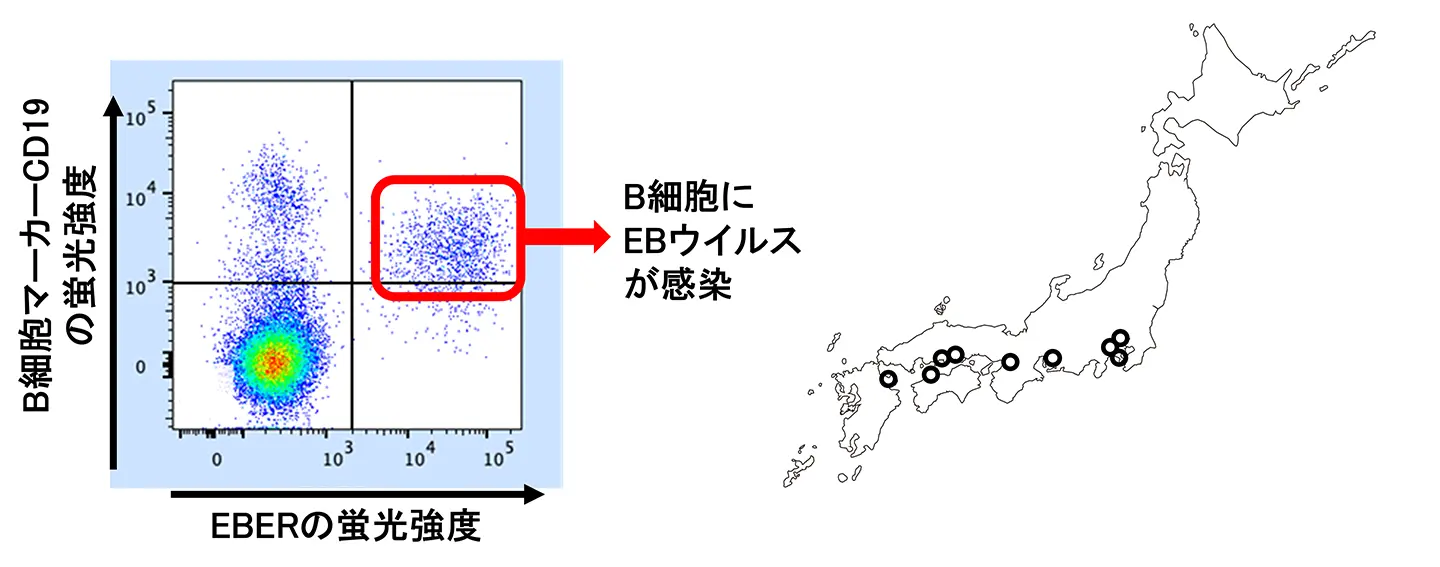
- 2025年6月末より試行的な解析が開始され、3ヵ月間で全国9施設の検体を解析
- T細胞・NK細胞・B細胞感染をそれぞれ特定
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/af52jq9t3alb
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=3011&prevId=&key=13c8ccc9582baac45564e453b554eb4a.pdf
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12185-024-03786-0
EBERフローFISHによるエプスタイン・バーウイルス感染細胞の高感度検出 Highly sensitive detection of Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells by EBER flow FISH
Dan Tomomasa,Kay Tanita,Yuriko Hiruma,Akihiro Hoshino,Ko Kudo,Shohei Azumi,Mitsutaka Shiota,Masayoshi Yamaoka,Katsuhide Eguchi,Masataka Ishimura,Yuka Tanaka,Keiji Iwatsuki,Keisuke Okuno,Asahito Hama,Ken-Ichi Sakamoto,Takashi Taga,Kimitoshi Goto,Haruka Ota,Akihiro Ichiki,Kaori Kanda,Takako Miyamura,Saori Endo,Hidenori Ohnishi,Yoji Sasahara,… Hirokazu Kanegane
International Journal of Hematology Published:03 May 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-024-03786-0
A Correction to this article was published on 16 December 2024
This article has been updated
Abstract
When Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection is suspected, identification of infected cells is important to understand the pathogenesis, determinine the treatment strategy, and predict the prognosis. We used the PrimeFlow™ RNA Assay Kit with a probe to detect EBV-encoded small RNAs (EBERs) and multiple surface markers, to identify EBV-infected cells by flow cytometry. We analyzed a total of 24 patients [11 with chronic active EBV disease (CAEBV), 3 with hydroa vacciniforme lymphoproliferative disorder, 2 with X-linked lymphoproliferative disease type 1 (XLP1), 2 with EBV-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, and 6 with posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder (PTLD)]. We compared infected cells using conventional quantitative PCR methods and confirmed that infected cell types were identical in most patients. Patients with CAEBV had widespread infection in T and NK cells, but a small amount of B cells were also infected, and infection in patients with XLP1 and PTLD was not limited to B cells. EBV-associated diseases are believed to be complex pathologies caused by EBV infecting a variety of cells other than B cells. We also demonstrated that infected cells were positive for HLA-DR in patients with CAEBV. EBER flow FISH can identify EBV-infected cells with high sensitivity and is useful for elucidating the pathogenesis.