2026-02-03 東京科学大学
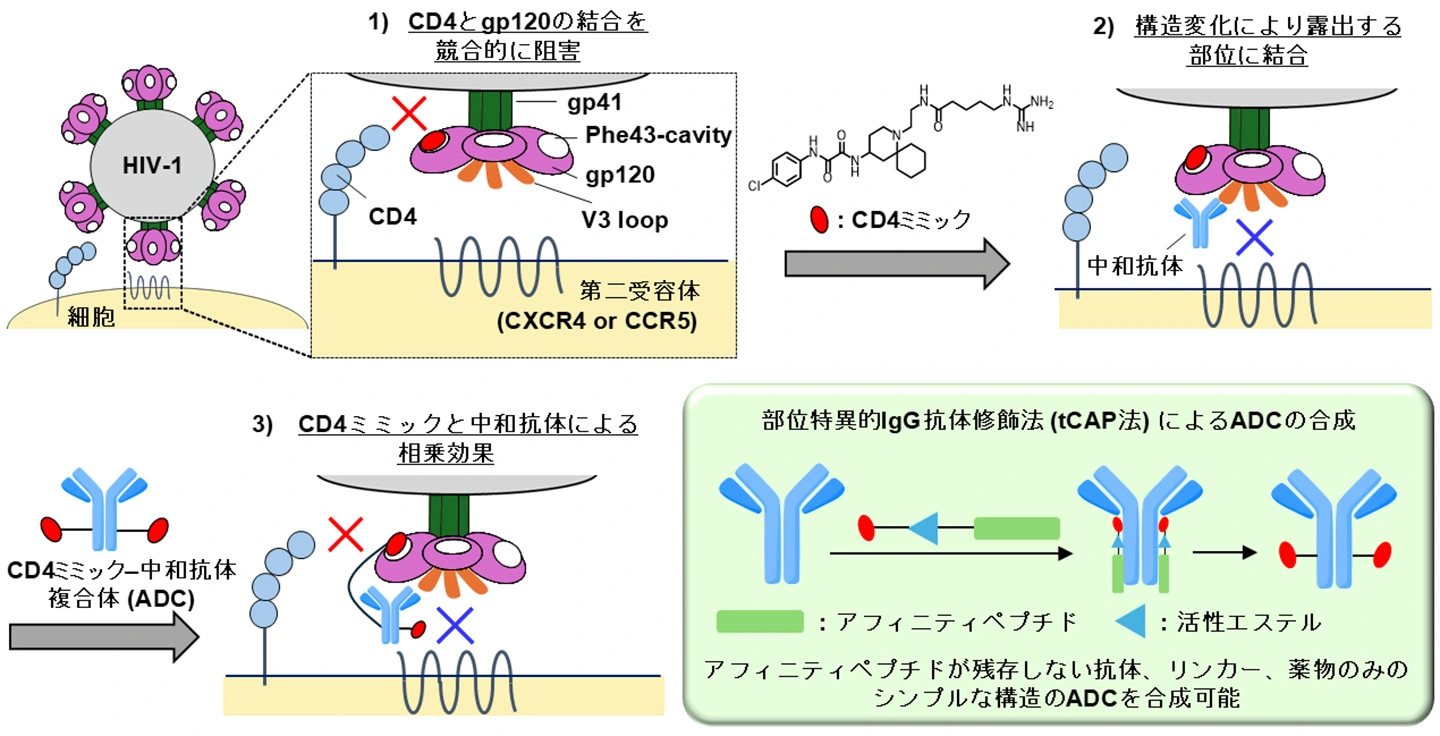
図1. HIVの細胞への侵入機構を標的としたCD4ミミックおよび中和抗体による感染阻害戦略。
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/7d5xpv2avoef
- https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cmdc.202500820
部位特異的修飾法によって合成されたCD4ミミック中和抗体複合体はHIV-1侵入阻害剤として有効である CD4 Mimic-Neutralizing Antibody Conjugates Synthesized by Site-Specific Modification Methods as HIV-1 Entry Inhibitors
Kohei Tsuji, Yutaro Miura, Takeo Kuwata, Riku Matsuzaki, Takuya Kobayakawa, Kaho Matsumoto, Yuji Ito, Taku Yoshiya, Shuzo Matsushita, Hirokazu Tamamura
ChemMedChem Published: 12 February 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/cmdc.202500820
Abstract
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) that equip multiple cytotoxic drugs on an antibody have been developed, particularly in cancer chemotherapy. In the treatment of viral infectious diseases, there are dominantly fewer examples of ADCs. Recently, we developed double-warhead ADCs targeting the entry of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) into host cells. One is a small molecule CD4 mimic, which is a competitive inhibitor against the interaction between a viral envelop protein, gp120, and a primary receptor, CD4, and the other is neutralizing antibodies, which recognize the regions of gp120, exposed by its conformational change after the interaction between gp120 and CD4. The conformational changes are also triggered by the binding of gp120 and a CD4 mimic, and therefore, the ADCs show positive effects on anti-HIV-1 activity compared to the combinational use of CD4 mimics with neutralizing antibodies. Herein, we synthesized novel ADCs containing a CD4 mimic and a neutralizing antibody, KD-247, using tCAP chemistry, which is based on a site-specific modification method for IgG antibodies, and evaluated their anti-HIV-1 and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) activities. As a result, the KD-247-adopted ADCs demonstrated enhanced anti-HIV-1 activities, whereas all of the ADCs reduced their ADCC activities.

