2022-03-28 エディンバラ大学
入院中の成人がCovid-19とインフルエンザに同時に感染した場合、Covid-19単独または他のウイルスに感染した患者と比較して、重症化および死亡のリスクが非常に高いことが、研究により明らかになりました。
<関連情報>
- https://www.ed.ac.uk/news/2022/covid-19-with-flu-increases-risk-of-severe-illness
- https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(22)00383-X/fulltext
SARS-CoV-2とインフルエンザウイルス、呼吸器合胞体ウイルス、アデノウイルスの同時感染。
SARS-CoV-2 co-infection with influenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus, or adenoviruses
Maaike C Swets,Clark D Russell,Ewen M Harrison,Annemarie B Docherty,Nazir Lone,Michelle Girvan,Hayley E Hardwick,ISARIC4C Investigators,Leonardus G Visser,Peter J M Openshaw,Geert H Groeneveld,Malcolm G Semple,J Kenneth Baillie,Show less
The Lancet Open AccessPublished:March 25, 2022 DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00383-X
Measures to reduce transmission of SARS-CoV-2 have also been effective in reducing the transmission of other endemic respiratory viruses.
As many countries decrease the use of such measures,
we expect that SARS-CoV-2 will circulate with other respiratory viruses, increasing the probability of co-infections.
The clinical outcome of respiratory viral co-infections with SARS-CoV-2 is unknown.
We examined clinical outcomes of co-infection with influenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus, or adenoviruses in 212 466 adults with SARS-CoV-2 infection who were admitted to hospital in the UK between Feb 6, 2020, and Dec 8, 2021, using the International Severe Acute Respiratory and Emerging Infection Consortium–WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol.
Details on patient recruitment, inclusion criteria, testing, and statistical analyses are included in the appendix (pp 2–3). Ethical approval was given by the South Central-Oxford C Research Ethics Committee in England (13/SC/0149), the Scotland A Research Ethics Committee (20/SS/0028), and the WHO Ethics Review Committee (RPC571 and RPC572, April, 2013).
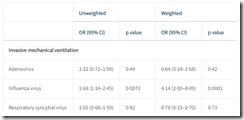
TableMultivariable model of the effect of co-infection compared with SARS-CoV-2 monoinfection
| Unweighted | Weighted | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p value | OR (95% CI) | p value | |
| Invasive mechanical ventilation | ||||
| Adenovirus | 1·22 (0·72–1·99) | 0·44 | 0·64 (0·18–1·68) | 0·42 |
| Influenza virus | 1·68 (1·14–2·45) | 0·0073 | 4·14 (2·00–8·49) | 0·0001 |
| Respiratory syncytial virus | 1·05 (0·68–1·59) | 0·82 | 0·78 (0·15–2·70) | 0·73 |
| In-hospital mortality | ||||
| Adenovirus | 1·60 (1·03–2·44) | 0·033 | 1·53 (0·67–3·33) | 0·29 |
| Influenza virus | 1·49 (1·04–2·12) | 0·027 | 2·35 (1·07–5·12) | 0·031 |
| Respiratory syncytial virus | 1·20 (0·84–1·72) | 0·31 | 0·60 (0·69–2·10) | 0·47 |
Model is adjusted for the following confounders: age, sex, number of comorbidities, treatment with corticosteroids, days since the start of the pandemic, co-infection, and 4C Mortality Score. OR=odds ratio.