ホルモン補充療法は、アルツハイマー型認知症を発症するリスクのある女性の予防に役立つ可能性があることが、新しい研究により明らかになりました。 Hormone Replacement Therapy could help prevent Alzheimer’s Dementia among women at risk of developing the disease, new research shows.
2023-01-16 エディンバラ大学
エジンバラ大学とイースト・アングリア大学の研究者らは、HRTは更年期の早い時期に導入することが最も効果的であることを発見しました。
研究チームは、参加者の脳の健康を長期にわたって調査するために設置された「欧州アルツハイマー病予防イニシアチブ」に参加した1,178人の女性のデータを調査しました。
このプロジェクトは10カ国にまたがり、参加者の脳を「健康」から認知症と診断されるまでの経過を追跡した。参加者は、50歳以上で認知症でない人が対象です。
専門家は、参加者が行った認知機能テストの結果を分析し、MRIによる脳の神経画像データを評価した。さらに、APOE4遺伝子を持つ人と持たない人のデータを比較する統計解析も行われた。
この研究結果は、『Alzheimer’s Research and Therapy』誌に掲載された。
<関連情報>
- https://www.ed.ac.uk/news/2023/hrt-could-ward-off-alzheimer-s-among-at-risk-women
- https://alzres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13195-022-01121-5
ホルモン補充療法は、リスクの高いAPOE4女性における認知機能の改善および脳体積の拡大に関連する:欧州アルツハイマー病予防(EPAD)コホートからの研究結果 Hormone replacement therapy is associated with improved cognition and larger brain volumes in at-risk APOE4 women: results from the European Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease (EPAD) cohort
Rasha N. M. Saleh,Michael Hornberger,Craig W. Ritchie & Anne Marie Minihane
Alzheimer’s Research and Therapy Published:09 January 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-022-01121-5
Abstract
Background
The risk of dementia is higher in women than men. The metabolic consequences of estrogen decline during menopause accelerate neuropathology in women. The use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) in the prevention of cognitive decline has shown conflicting results. Here we investigate the modulating role of APOE genotype and age at HRT initiation on the heterogeneity in cognitive response to HRT.
Methods
The analysis used baseline data from participants in the European Prevention of Alzheimer’s Dementia (EPAD) cohort (total n= 1906, women= 1178, 61.8%). Analysis of covariate (ANCOVA) models were employed to test the independent and interactive impact of APOE genotype and HRT on select cognitive tests, such as MMSE, RBANS, dot counting, Four Mountain Test (FMT), and the supermarket trolley test (SMT), together with volumes of the medial temporal lobe (MTL) regions by MRI. Multiple linear regression models were used to examine the impact of age of HRT initiation according to APOE4 carrier status on these cognitive and MRI outcomes.
Results
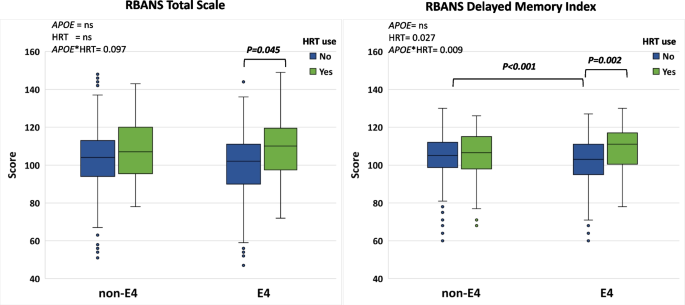
APOE4 HRT users had the highest RBANS delayed memory index score (P-APOE*HRT interaction = 0.009) compared to APOE4 non-users and to non-APOE4 carriers, with 6–10% larger entorhinal (left) and amygdala (right and left) volumes (P-interaction= 0.002, 0.003, and 0.005 respectively). Earlier introduction of HRT was associated with larger right (standardized β= -0.555, p=0.035) and left hippocampal volumes (standardized β= -0.577, p=0.028) only in APOE4 carriers.
Conclusion
HRT introduction is associated with improved delayed memory and larger entorhinal and amygdala volumes in APOE4 carriers only. This may represent an effective targeted strategy to mitigate the higher life-time risk of AD in this large at-risk population subgroup. Confirmation of findings in a fit for purpose RCT with prospective recruitment based on APOE genotype is needed to establish causality.