UCアーバイン校の発見が精神疾患の新たな治療標的を提供する UC Irvine discovery offers new therapeutic target for treating mental illness
2023-02-27 カリフォルニア大学校アーバイン校(UCI)
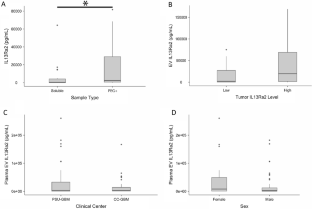
報酬回路の機能不全は、うつ病、薬物乱用、過度のリスクテイキングなど、いくつかの主要な疾患の原因と考えられています。研究では、マウスを用いて報酬行動を妨げることができる新しい神経回路が発見され、その回路を抑制することで正常な報酬行動が回復することが示されました。また、この仕組みが男性と女性で異なる影響を与える可能性があることが指摘されました。
<関連情報>
- https://news.uci.edu/2023/02/27/early-life-stress-can-disrupt-maturation-of-brains-reward-circuits-promoting-disorders/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-36780-x
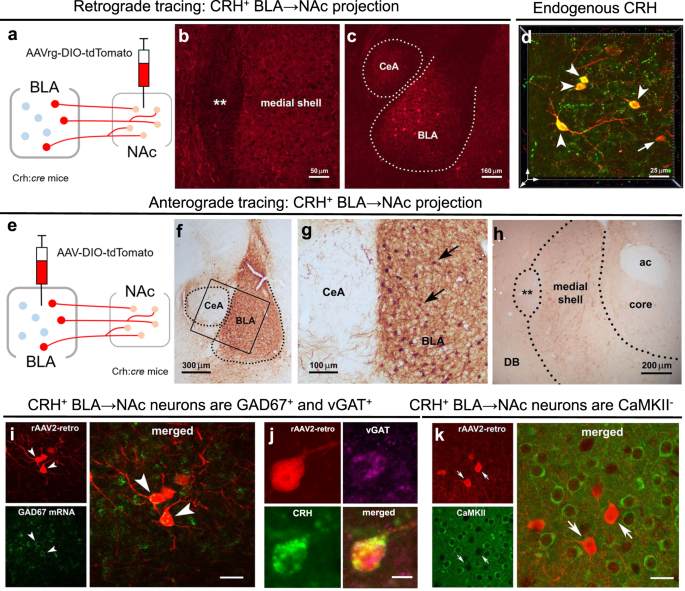
ストレスによるCRH/GABAプロジェクションの可塑性がマウスの報酬行動を阻害することを発見 Stress-induced plasticity of a CRH/GABA projection disrupts reward behaviors in mice
Matthew T. Birnie,Annabel K. Short,Gregory B. de Carvalho,Lara Taniguchi,Benjamin G. Gunn,Aidan L. Pham,Christy A. Itoga,Xiangmin Xu,Lulu Y. Chen,Stephen V. Mahler,Yuncai Chen & Tallie Z. Baram
Nature Communications Published:25 February 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36780-x
Abstract
Disrupted operations of the reward circuit underlie major emotional disorders, including depression, which commonly arise following early life stress / adversity (ELA). However, how ELA enduringly impacts reward circuit functions remains unclear. We characterize a stress-sensitive projection connecting basolateral amygdala (BLA) and nucleus accumbens (NAc) that co-expresses GABA and the stress-reactive neuropeptide corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH). We identify a crucial role for this projection in executing disrupted reward behaviors provoked by ELA: chemogenetic and optogenetic stimulation of the projection in control male mice suppresses several reward behaviors, recapitulating deficits resulting from ELA and demonstrating the pathway’s contributions to normal reward behaviors. In adult ELA mice, inhibiting–but not stimulating–the projection, restores typical reward behaviors yet has little effect in controls, indicating ELA-induced maladaptive plasticity of this reward-circuit component. Thus, we discover a stress-sensitive, reward inhibiting BLA → NAc projection with unique molecular features, which may provide intervention targets for disabling mental illnesses.