2023-04-19 カリフォルニア大学リバーサイド校(UCR)
研究結果は、「Frontiers in Neuroscience」に掲載されました。
研究は哺乳期のアルコール暴露を中心に行われ、母親マウスの授乳によって子供がアルコールに曝露された場合、早期の発達段階で体重、脳の成長が抑制され、行動発達も異常なストレス調節や高リスク行動などが生じることが分かりました。
研究チームは、赤ちゃんの発育に悪影響を及ぼすため、母親が哺乳期中にアルコールを摂取しないことを推奨しています。
<関連情報>
- https://news.ucr.edu/articles/2023/04/19/boozing-while-breastfeeding-impacts-health-newborns
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnins.2023.1147274/full
アルコールと哺乳期: マウスモデルにおける発達障害
Alcohol and lactation: Developmental deficits in a mouse model
Roberto F. Perez Jr, Kathleen E. Conner, Michael A. Erickson, Mirembe Nabatanzi and Kelly J. Huffman
Frontiers in Neuroscience published:13 March 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2023.1147274
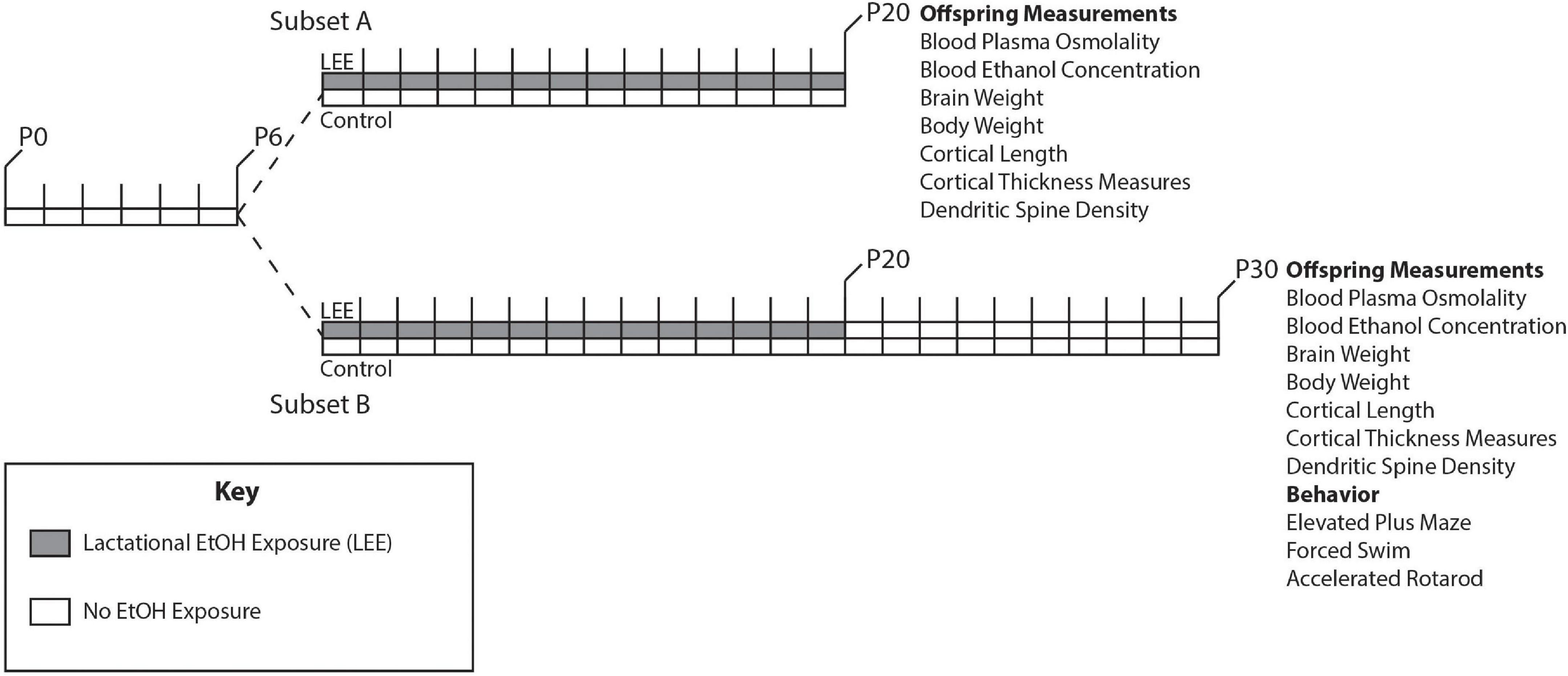
It is well documented that prenatal ethanol exposure via maternal consumption of alcohol during pregnancy alters brain and behavioral development in offspring. Thus, the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) advises against maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy. However, little emphasis has been placed on educating new parents about alcohol consumption while breastfeeding. This is partly due to a paucity of research on lactational ethanol exposure (LEE) effects in children; although, it has been shown that infants exposed to ethanol via breast milk frequently present with reduced body mass, low verbal IQ scores, and altered sleeping patterns. As approximately 36% of breastfeeding mothers in the US consume alcohol, continued research in this area is critical. Our study employed a novel murine LEE model, where offspring were exposed to ethanol via nursing from postnatal day (P) 6 through P20, a period correlated with infancy in humans. Compared to controls, LEE mice had reduced body weights and neocortical lengths at P20 and P30. Brain weights were also reduced in both ages in males, and at P20 for females, however, female brain weights recovered to control levels by P30. We investigated neocortical features and found that frontal cortex thickness was reduced in LEE males compared to controls. Analyses of dendritic spines in the prelimbic subdivision of medial prefrontal cortex revealed a trend of reduced densities in LEE mice. Results of behavioral tests suggest that LEE mice engage in higher risk-taking behavior, show abnormal stress regulation, and exhibit increased hyperactivity. In summary, our data describe potential adverse brain and behavioral developmental outcomes due to LEE. Thus, women should be advised to refrain from consuming alcohol during breastfeeding until additional research can better guide recommendations of safe maternal practices in early infancy.


