2023-04-17 ミシガン大学
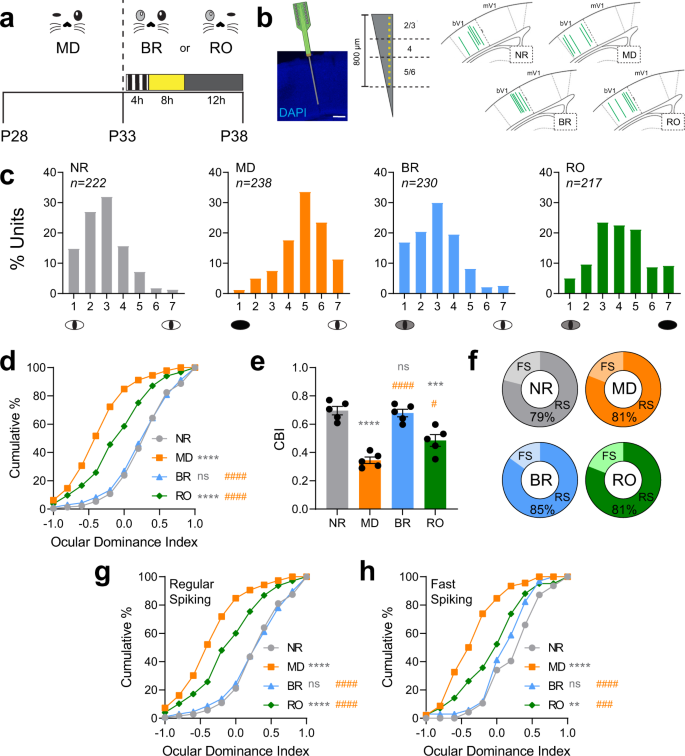
研究者らは、対象としたマウスにビデオ映像のような視覚的刺激を与え、弱い目を閉じて強い目だけを使う治療法と、両眼を同時に使う治療法を比較した。その結果、両眼を同時に使う治療法がより脳可塑性を高め、睡眠をとることで治療効果がより高まることがわかった。
これにより、従来の目をふさぐ治療法よりも、両眼を使う治療法がより優れている可能性があり、睡眠をとるタイミングを考慮することが治療効果を高めることにつながるとされる。
<関連情報>
- https://news.umich.edu/binocular-treatment-helps-with-a-common-vision-problem-sleep-makes-it-stick/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-023-04798-y
弱視モデルマウスにおいて、豊かな両眼体験と睡眠が両眼視皮質反応を最適に回復させる Enriched binocular experience followed by sleep optimally restores binocular visual cortical responses in a mouse model of amblyopia
Jessy D. Martinez,Marcus J. Donnelly,Donald S. Popke,Daniel Torres,Lydia G. Wilson,William P. Brancaleone,Sarah Sheskey,Cheng-mao Lin,Brittany C. Clawson,Sha Jiang & Sara J. Aton
Communications Biology Published:13 April 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-023-04798-y
Abstract
Studies of primary visual cortex have furthered our understanding of amblyopia, long-lasting visual impairment caused by imbalanced input from the two eyes during childhood, which is commonly treated by patching the dominant eye. However, the relative impacts of monocular vs. binocular visual experiences on recovery from amblyopia are unclear. Moreover, while sleep promotes visual cortex plasticity following loss of input from one eye, its role in recovering binocular visual function is unknown. Using monocular deprivation in juvenile male mice to model amblyopia, we compared recovery of cortical neurons’ visual responses after identical-duration, identical-quality binocular or monocular visual experiences. We demonstrate that binocular experience is quantitatively superior in restoring binocular responses in visual cortex neurons. However, this recovery was seen only in freely-sleeping mice; post-experience sleep deprivation prevented functional recovery. Thus, both binocular visual experience and subsequent sleep help to optimally renormalize bV1 responses in a mouse model of amblyopia.


