2023-05-01 カリフォルニア大学バークレー校(UCB)
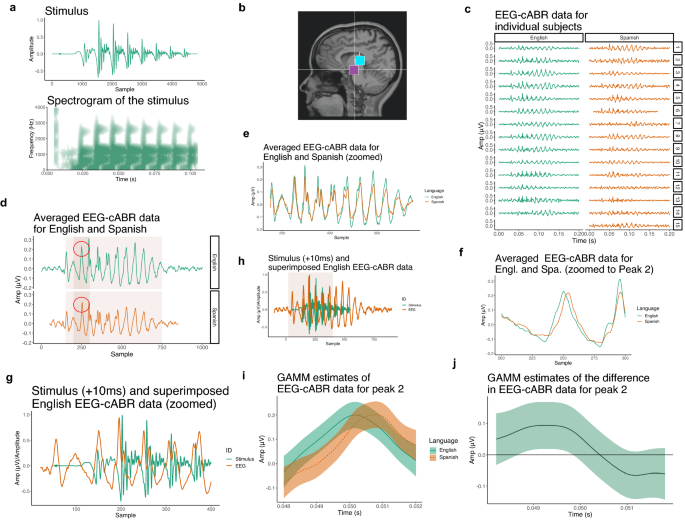
研究者らは、参加者の頭に電極を配置し、「bah」という単一音節を聞いた際の脳波を測定し、それを英語を学習するために訓練されたAIシステムが生成する信号と比較した。比較結果は非常に類似しており、研究者たちはこれが処理の類似性を示していると述べている。
これは、AIシステムが日常生活の中でますます不可欠になっている現在、健康管理から教育までのさまざまな分野において重要になっている。
<関連情報>
- https://news.berkeley.edu/2023/05/01/raw-data-show-ai-signals-mirror-how-the-brain-listens-and-learns/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-023-33384-9
言語経験に基づく畳み込み層と脳幹における音声の符号化 Encoding of speech in convolutional layers and the brain stem based on language experience
Gašper Beguš,Alan Zhou & T. Christina Zhao
Scientific Reports Published:20 April 2023
DO:Ihttps://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-33384-9
Abstract
Comparing artificial neural networks with outputs of neuroimaging techniques has recently seen substantial advances in (computer) vision and text-based language models. Here, we propose a framework to compare biological and artificial neural computations of spoken language representations and propose several new challenges to this paradigm. The proposed technique is based on a similar principle that underlies electroencephalography (EEG): averaging of neural (artificial or biological) activity across neurons in the time domain, and allows to compare encoding of any acoustic property in the brain and in intermediate convolutional layers of an artificial neural network. Our approach allows a direct comparison of responses to a phonetic property in the brain and in deep neural networks that requires no linear transformations between the signals. We argue that the brain stem response (cABR) and the response in intermediate convolutional layers to the exact same stimulus are highly similar without applying any transformations, and we quantify this observation. The proposed technique not only reveals similarities, but also allows for analysis of the encoding of actual acoustic properties in the two signals: we compare peak latency (i) in cABR relative to the stimulus in the brain stem and in (ii) intermediate convolutional layers relative to the input/output in deep convolutional networks. We also examine and compare the effect of prior language exposure on the peak latency in cABR and in intermediate convolutional layers. Substantial similarities in peak latency encoding between the human brain and intermediate convolutional networks emerge based on results from eight trained networks (including a replication experiment). The proposed technique can be used to compare encoding between the human brain and intermediate convolutional layers for any acoustic property and for other neuroimaging techniques.