2023-07-07 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
 © 2023 EPFL
© 2023 EPFL
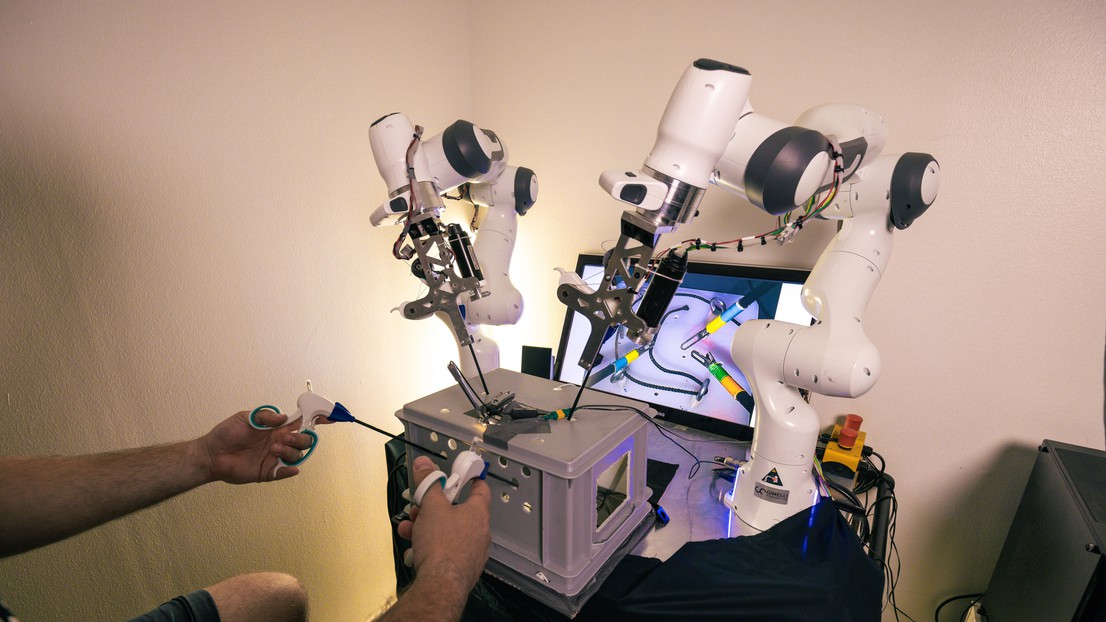
◆このシステムは既に専門家によって試験され、ジュネーブで臨床試験が進行中です。共有制御の下、ロボットは外科医の動きを予測しながら器具を制御し、手術の負担を軽減し、パフォーマンスと協調性を向上させます。これにより、4本の腕を同時に操作する腹腔鏡手術が可能となり、手術結果の向上が期待されています。
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/robot-assisted-surgery-four-arms-are-better-than-t/
- https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/02783649231180366
足の触覚インターフェイスを介して2つのロボットアシスタントを制御することにより、4アーム腹腔鏡手術を可能にする Enabling four-arm laparoscopic surgery by controlling two robotic assistants via haptic foot interfaces
Jacob Hernandez Sanchez, Walid Amanhoud, Aude Billard, and Mohamed Bouri
The International Journal of Robotics Research Published:June 19, 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1177/02783649231180366
Abstract
Robotic surgery is a promising direction to improve surgeons and assistants’ daily life with respect to conventional surgery. In this work, we propose solo laparoscopic surgery in which two robotic arms, controlled via haptic foot interfaces, assist the task of the hands. Such a system opens the door for simultaneous control of four laparoscopic tools by the same user. Each hand controls a manipulative tool while a foot controls an endoscope/camera and another controls an actuated gripper. In this scenario, the surgeon and robots need to work collaboratively within a concurrent workspace, while meeting the precision demands of surgery. To this end, we propose a control framework for the robotic arms that deals with all the task- and safety-related constraints. Furthermore, to ease the control through the feet, two assistance modalities are proposed: adaptive visual tracking of the laparoscopic instruments with the camera and grasping assistance for the gripper. A user study is conducted on twelve subjects to highlight the ease of use of the system and to evaluate the relevance of the proposed shared control strategies. The results confirm the feasibility of four-arm surgical-like tasks without extensive training in tasks that involve visual-tracking and manipulation goals for the feet, as well as coordination with both hands. Moreover, our study characterizes and motivates the use of robotic assistance for reducing task load, improving performance, increasing fluency, and eliciting higher coordination during four-arm laparoscopic tasks.