2023-09-20 ワシントン大学セントルイス校
◆この段階に介入することで、脳損傷を引き起こす一連の出来事を阻止できる可能性があり、タウオパチーの新たな治療法の展望が開けました。研究では、lncRNAと呼ばれるRNA分子の一群がタウオパチーの共通の病態過程に影響を与え、治療への新たなアプローチを提供する可能性が示されました。
<関連情報>
- https://source.wustl.edu/2023/09/how-do-toxic-proteins-accumulate-in-alzheimers-and-other-diseases/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41380-023-02237-2
ロングノンコーディングRNA SNHG8がタウオパチーにおけるストレス顆粒の形成を促進する Long non-coding RNA SNHG8 drives stress granule formation in tauopathies
Reshma Bhagat,Miguel A. Minaya,Arun Renganathan,Muneshwar Mehra,Jacob Marsh,Rita Martinez,Abdallah M. Eteleeb,Alissa L. Nana,Salvatore Spina,William W. Seeley,Lea T. Grinberg & Celeste M. Karch
Molecular Psychiatry Published:21 September 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-023-02237-2
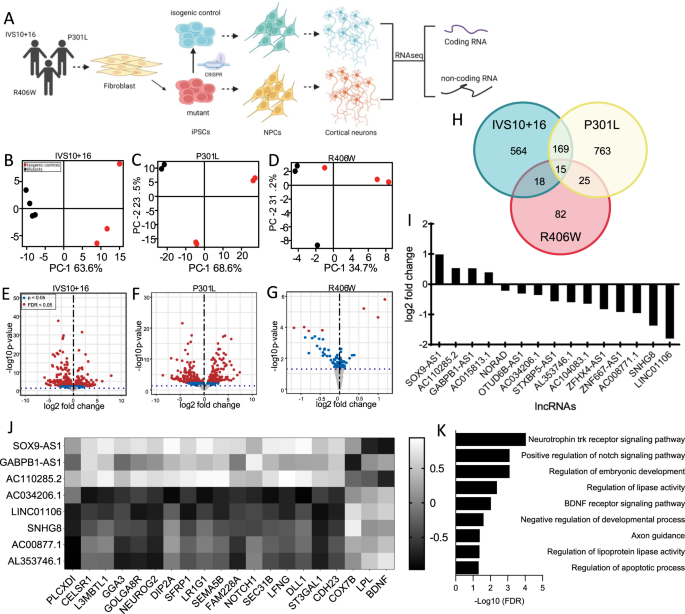
Abstract
Tauopathies are a heterogenous group of neurodegenerative disorders characterized by tau aggregation in the brain. In a subset of tauopathies, rare mutations in the MAPT gene, which encodes the tau protein, are sufficient to cause disease; however, the events downstream of MAPT mutations are poorly understood. Here, we investigate the role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), transcripts >200 nucleotides with low/no coding potential that regulate transcription and translation, and their role in tauopathy. Using stem cell derived neurons from patients carrying a MAPT p.P301L, IVS10 + 16, or p.R406W mutation and CRISPR-corrected isogenic controls, we identified transcriptomic changes that occur as a function of the MAPT mutant allele. We identified 15 lncRNAs that were commonly differentially expressed across the three MAPT mutations. The commonly differentially expressed lncRNAs interact with RNA-binding proteins that regulate stress granule formation. Among these lncRNAs, SNHG8 was significantly reduced in a mouse model of tauopathy and in FTLD-tau, progressive supranuclear palsy, and Alzheimer’s disease brains. We show that SNHG8 interacts with tau and stress granule-associated RNA-binding protein TIA1. Overexpression of mutant tau in vitro is sufficient to reduce SNHG8 expression and induce stress granule formation. Rescuing SNHG8 expression leads to reduced stress granule formation and reduced TIA1 levels in immortalized cells and in MAPT mutant neurons, suggesting that dysregulation of this non-coding RNA is a causal factor driving stress granule formation via TIA1 in tauopathies.


