2023-12-19 ピッツバーグ大学
◆C diffは下痢と大腸の炎症(大腸炎)を引き起こし、米国では年間約50万件の感染症の原因となっています。オマダサイクリンはC diffを引き起こす可能性が低いと臨床試験で示されていましたが、その理由はわかっていませんでした。
◆研究者は、オマダサイクリンが口から投与された場合に、腸内で高濃度になり、大腸に住む健康な細菌叢である腸内細菌叢に及ぼす影響を調査しました。結果は「The Journal of Infectious Diseases」に掲載されました。
<関連情報>
- https://uh.edu/news-events/stories/2023/december-2023/12292023-garey-cdiff-new-antibiotic-omadacycline.php
- https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiad537/7458919
健康なボランティアにおける経口オマダサイクリンとバンコマイシンの糞便薬物動態と腸内細菌叢への影響 Fecal Pharmacokinetics and Gut Microbiome Effects of Oral Omadacycline Versus Vancomycin in Healthy Volunteers
Jinhee Jo, Chenlin Hu, Khurshida Begum, Weiqun Wang, Thanh M Le, Samantha Agyapong, Blake M Hanson, Hossaena Ayele, Chris Lancaster, M Jahangir Alam,Anne J Gonzales-Luna, Kevin W Garey
The Journal of Infectious Diseases Published:05 December 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiad537
Abstract
Background
Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) is a common healthcare-associated infection with limited treatment options. Omadacycline, an aminomethylcycline tetracycline, has potent in vitro activity against C difficile and a low propensity to cause CDI in clinical trials. We aimed to assess fecal pharmacokinetics and gut microbiome effects of oral omadacycline compared to oral vancomycin in healthy adults.
Methods
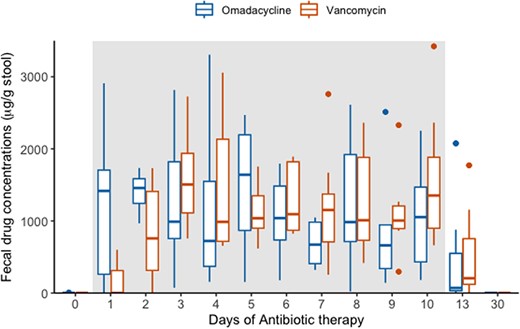
This was a phase 1, nonblinded, randomized clinical trial conducted in healthy volunteers aged 18–40 years. Subjects received a 10-day course of omadacycline or vancomycin. Stool samples were collected at baseline, daily during therapy, and at follow-up visits. Omadacycline and vancomycin stool concentrations were assessed, and microbiome changes were compared.
Results
Sixteen healthy volunteers with a mean age of 26 (standard deviation [SD], 5) years were enrolled; 62.5% were male, and participants’ mean body mass index was 23.5 (SD, 4.0) kg/m2. Omadacycline was well tolerated with no safety signal differences between the 2 antibiotics. A rapid initial increase in fecal concentrations of omadacycline was observed compared to vancomycin, with maximum concentrations achieved within 48 hours. A significant difference in alpha diversity was observed following therapy in both the omadacycline and vancomycin groups (P < .05). Bacterial abundance and beta diversity analysis showed differing microbiome changes in subjects who received omadacycline versus vancomycin.
Conclusions
Subjects given omadacycline had high fecal concentrations with a distinct microbiome profile compared to vancomycin.
Clinical Trials Registration
NCT06030219.