2024-02-21 ミュンヘン大学(LMU)
<関連情報>
- https://www.lmu.de/en/newsroom/news-overview/news/possible-trigger-for-autoimmune-diseases-discovered.html
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07079-8
B細胞が視神経脊髄炎自己抗原AQP4に対する寛容を制御する B cells orchestrate tolerance to the neuromyelitis optica autoantigen AQP4
Ali Maisam Afzali,Lucy Nirschl,Christopher Sie,Monika Pfaller,Oleksii Ulianov,Tobias Hassler,Christine Federle,Elisabetta Petrozziello,Sudhakar Reddy Kalluri,Hsin Hsiang Chen,Sofia Tyystjärvi,Andreas Muschaweckh,Katja Lammens,Claire Delbridge,Andreas Büttner,Katja Steiger,Gönül Seyhan,Ole Petter Ottersen,Rupert Öllinger,Roland Rad,Sebastian Jarosch,Adrian Straub,Anton Mühlbauer,Simon Grassmann,… Thomas Korn
Nature Published:21 February 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07079-8
Abstract
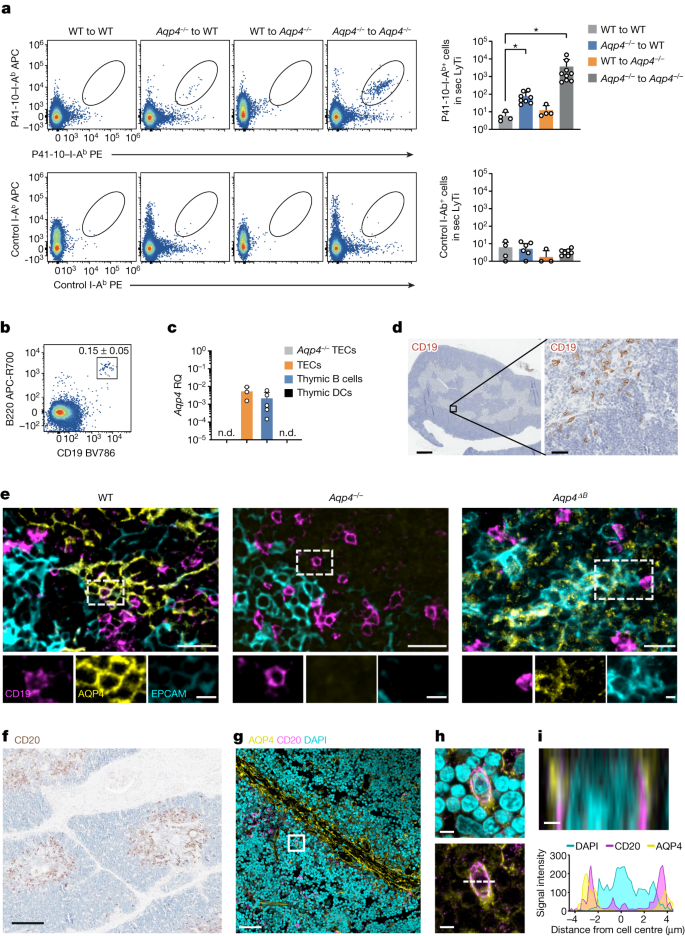
Neuromyelitis optica is a paradigmatic autoimmune disease of the central nervous system, in which the water-channel protein AQP4 is the target antigen1. The immunopathology in neuromyelitis optica is largely driven by autoantibodies to AQP42. However, the T cell response that is required for the generation of these anti-AQP4 antibodies is not well understood. Here we show that B cells endogenously express AQP4 in response to activation with anti-CD40 and IL-21 and are able to present their endogenous AQP4 to T cells with an AQP4-specific T cell receptor (TCR). A population of thymic B cells emulates a CD40-stimulated B cell transcriptome, including AQP4 (in mice and humans), and efficiently purges the thymic TCR repertoire of AQP4-reactive clones. Genetic ablation of Aqp4 in B cells rescues AQP4-specific TCRs despite sufficient expression of AQP4 in medullary thymic epithelial cells, and B-cell-conditional AQP4-deficient mice are fully competent to raise AQP4-specific antibodies in productive germinal-centre responses. Thus, the negative selection of AQP4-specific thymocytes is dependent on the expression and presentation of AQP4 by thymic B cells. As AQP4 is expressed in B cells in a CD40-dependent (but not AIRE-dependent) manner, we propose that thymic B cells might tolerize against a group of germinal-centre-associated antigens, including disease-relevant autoantigens such as AQP4.