2024-04-11 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/a-new-tool-for-tracing-the-family-trees-of-cells/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-47158-y
scRNA-seqデータセットからの遺伝子発現記憶に基づく細胞系列の予測 Gene-expression memory-based prediction of cell lineages from scRNA-seq datasets
A. S. Eisele,M. Tarbier,A. A. Dormann,V. Pelechano & D. M. Suter
Nature Communications Published:29 March 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-47158-y
Abstract
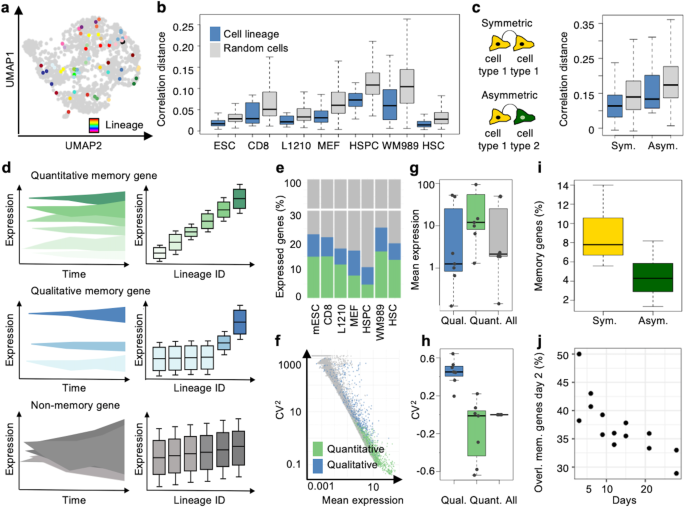
Assigning single cell transcriptomes to cellular lineage trees by lineage tracing has transformed our understanding of differentiation during development, regeneration, and disease. However, lineage tracing is technically demanding, often restricted in time-resolution, and most scRNA-seq datasets are devoid of lineage information. Here we introduce Gene Expression Memory-based Lineage Inference (GEMLI), a computational tool allowing to robustly identify small to medium-sized cell lineages solely from scRNA-seq datasets. GEMLI allows to study heritable gene expression, to discriminate symmetric and asymmetric cell fate decisions and to reconstruct individual multicellular structures from pooled scRNA-seq datasets. In human breast cancer biopsies, GEMLI reveals previously unknown gene expression changes at the onset of cancer invasiveness. The universal applicability of GEMLI allows studying the role of small cell lineages in a wide range of physiological and pathological contexts, notably in vivo. GEMLI is available as an R package on GitHub (https://github.com/UPSUTER/GEMLI).