2024-04-24 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/mini-colons-revolutionize-colorectal-cancer-resear/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07330-2
大腸癌の発生をミニ結腸を用いて時空間的に解明 Spatiotemporally resolved colorectal oncogenesis in mini-colons ex vivo
L. Francisco Lorenzo-Martín,Tania Hübscher,Amber D. Bowler,Nicolas Broguiere,Jakob Langer,Lucie Tillard,Mikhail Nikolaev,Freddy Radtke & Matthias P. Lutolf
Nature Published:24 April 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07330-2
Abstract
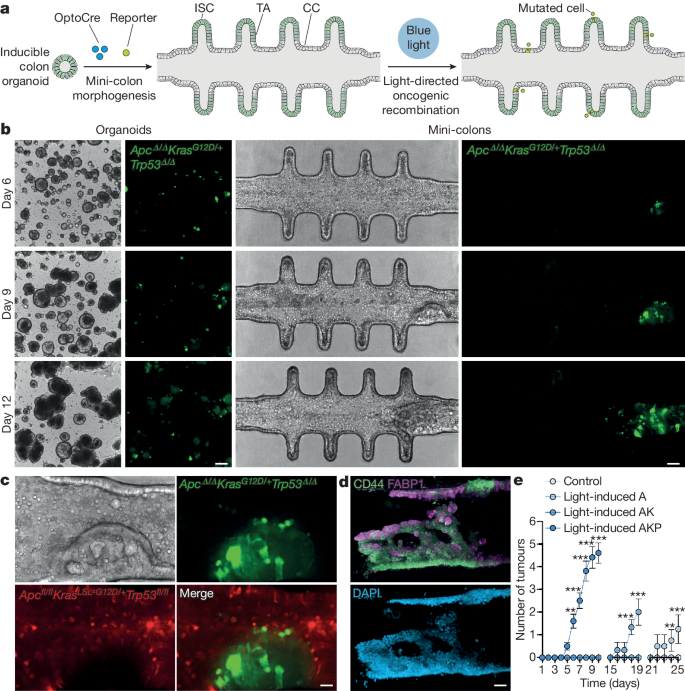
Three-dimensional organoid culture technologies have revolutionized cancer research by allowing for more realistic and scalable reproductions of both tumour and microenvironmental structures1,2,3. This has enabled better modelling of low-complexity cancer cell behaviours that occur over relatively short periods of time4. However, available organoid systems do not capture the intricate evolutionary process of cancer development in terms of tissue architecture, cell diversity, homeostasis and lifespan. As a consequence, oncogenesis and tumour formation studies are not possible in vitro and instead require the extensive use of animal models, which provide limited spatiotemporal resolution of cellular dynamics and come at a considerable cost in terms of resources and animal lives. Here we developed topobiologically complex mini-colons that are able to undergo tumorigenesis ex vivo by integrating microfabrication, optogenetic and tissue engineering approaches. With this system, tumorigenic transformation can be spatiotemporally controlled by directing oncogenic activation through blue-light exposure, and emergent colon tumours can be tracked in real-time at the single-cell resolution for several weeks without breaking the culture. These induced mini-colons display rich intratumoural and intertumoural diversity and recapitulate key pathophysiological hallmarks displayed by colorectal tumours in vivo. By fine-tuning cell-intrinsic and cell-extrinsic parameters, mini-colons can be used to identify tumorigenic determinants and pharmacological opportunities. As a whole, our study paves the way for cancer initiation research outside living organisms.