2024-04-30 カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/new-drug-candidate-reverses-obesity-in-mice
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s42255-024-01038-3
哺乳類のmtDNA転写の阻害は逆説的に作用し、食事誘発性肝肉食と肥満を逆転させる Inhibition of mammalian mtDNA transcription acts paradoxically to reverse diet-induced hepatosteatosis and obesity
Shan Jiang,Taolin Yuan,Florian A. Rosenberger,Arnaud Mourier,Nathalia R. V. Dragano,Laura S. Kremer,Diana Rubalcava-Gracia,Fynn M. Hansen,Melissa Borg,Mara Mennuni,Roberta Filograna,David Alsina,Jelena Misic,Camilla Koolmeister,Polyxeni Papadea,Martin Hrabe de Angelis,Lipeng Ren,Olov Andersson,Anke Unger,Tim Bergbrede,Raffaella Di Lucrezia,Rolf Wibom,Juleen R. Zierath,Anna Krook,… Nils-Göran Larsson
Nature Metabolism Published:30 April 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-024-01038-3
Abstract
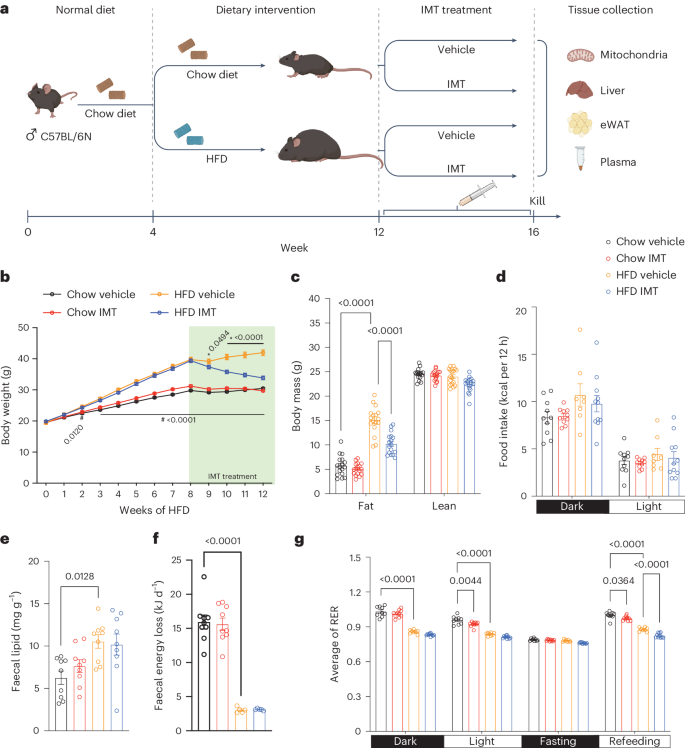
The oxidative phosphorylation system1 in mammalian mitochondria plays a key role in transducing energy from ingested nutrients2. Mitochondrial metabolism is dynamic and can be reprogrammed to support both catabolic and anabolic reactions, depending on physiological demands or disease states. Rewiring of mitochondrial metabolism is intricately linked to metabolic diseases and promotes tumour growth3,4,5. Here, we demonstrate that oral treatment with an inhibitor of mitochondrial transcription (IMT)6 shifts whole-animal metabolism towards fatty acid oxidation, which, in turn, leads to rapid normalization of body weight, reversal of hepatosteatosis and restoration of normal glucose tolerance in male mice on a high-fat diet. Paradoxically, the IMT treatment causes a severe reduction of oxidative phosphorylation capacity concomitant with marked upregulation of fatty acid oxidation in the liver, as determined by proteomics and metabolomics analyses. The IMT treatment leads to a marked reduction of complex I, the main dehydrogenase feeding electrons into the ubiquinone (Q) pool, whereas the levels of electron transfer flavoprotein dehydrogenase and other dehydrogenases connected to the Q pool are increased. This rewiring of metabolism caused by reduced mtDNA expression in the liver provides a principle for drug treatment of obesity and obesity-related pathology.