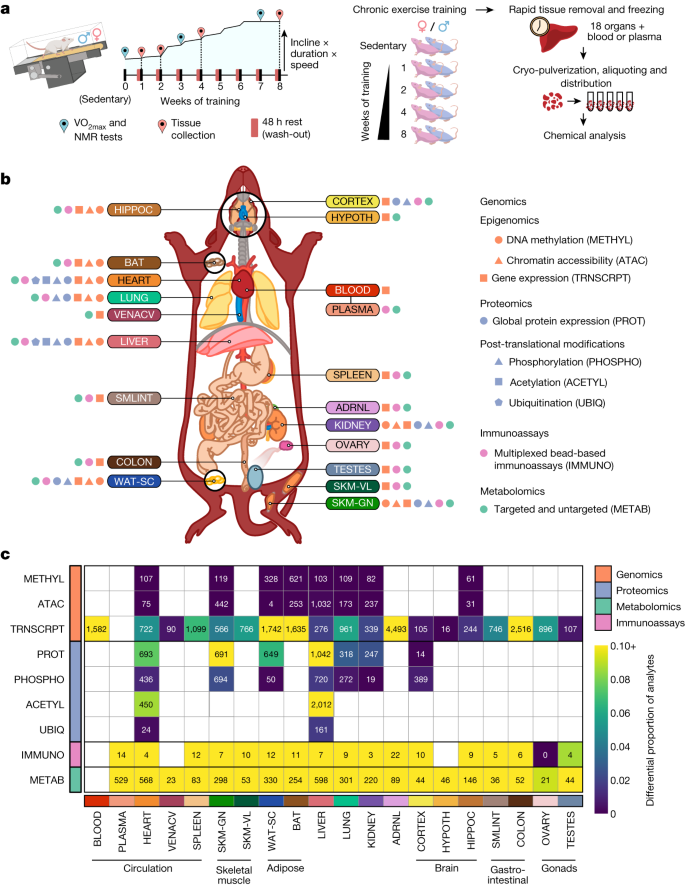
2024-05-01 ワシントン州立大学(WSU)
<関連情報>
- https://news.wsu.edu/press-release/2024/05/01/chatgpt-fails-at-heart-risk-assessment/
- https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0301854
ChatGPTは外傷性胸痛患者のリスク層別化に一貫性がない ChatGPT provides inconsistent risk-stratification of patients with atraumatic chest pain
Thomas F. Heston ,Lawrence M. Lewis
PLOS ONE Published: April 16, 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0301854
Abstract
Background
ChatGPT-4 is a large language model with promising healthcare applications. However, its ability to analyze complex clinical data and provide consistent results is poorly known. Compared to validated tools, this study evaluated ChatGPT-4’s risk stratification of simulated patients with acute nontraumatic chest pain.
Methods
Three datasets of simulated case studies were created: one based on the TIMI score variables, another on HEART score variables, and a third comprising 44 randomized variables related to non-traumatic chest pain presentations. ChatGPT-4 independently scored each dataset five times. Its risk scores were compared to calculated TIMI and HEART scores. A model trained on 44 clinical variables was evaluated for consistency.
Results
ChatGPT-4 showed a high correlation with TIMI and HEART scores (r = 0.898 and 0.928, respectively), but the distribution of individual risk assessments was broad. ChatGPT-4 gave a different risk 45–48% of the time for a fixed TIMI or HEART score. On the 44-variable model, a majority of the five ChatGPT-4 models agreed on a diagnosis category only 56% of the time, and risk scores were poorly correlated (r = 0.605).
Conclusion
While ChatGPT-4 correlates closely with established risk stratification tools regarding mean scores, its inconsistency when presented with identical patient data on separate occasions raises concerns about its reliability. The findings suggest that while large language models like ChatGPT-4 hold promise for healthcare applications, further refinement and customization are necessary, particularly in the clinical risk assessment of atraumatic chest pain patients.