2024-05-14 カリフォルニア大学サンディエゴ校(UCSD)
<関連情報>
- https://today.ucsd.edu/story/music-map-reveals-some-brain-cells-age-faster-and-are-more-prevalent-in-alzheimers
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07239-w
加齢ヒト脳におけるシングルセル・マルチプレックス・クロマチン・RNA相互作用 Single-cell multiplex chromatin and RNA interactions in ageing human brain
Xingzhao Wen,Zhifei Luo,Wenxin Zhao,Riccardo Calandrelli,Tri C. Nguyen,Xueyi Wan,John Lalith Charles Richard & Sheng Zhong
Nature Published:27 March 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07239-w
Abstract
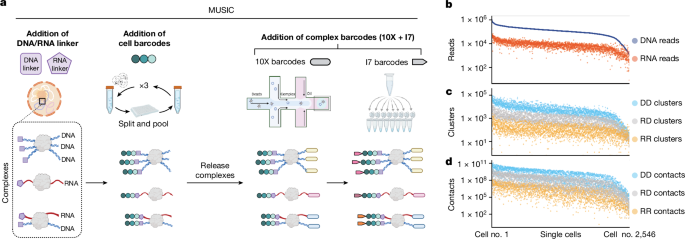
Dynamically organized chromatin complexes often involve multiplex chromatin interactions and sometimes chromatin-associated RNA1,2,3. Chromatin complex compositions change during cellular differentiation and ageing, and are expected to be highly heterogeneous among terminally differentiated single cells4,5,6,7. Here we introduce the multinucleic acid interaction mapping in single cells (MUSIC) technique for concurrent profiling of multiplex chromatin interactions, gene expression and RNA–chromatin associations within individual nuclei. When applied to 14 human frontal cortex samples from older donors, MUSIC delineated diverse cortical cell types and states. We observed that nuclei exhibiting fewer short-range chromatin interactions were correlated with both an ‘older’ transcriptomic signature and Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Furthermore, the cell type exhibiting chromatin contacts between cis expression quantitative trait loci and a promoter tends to be that in which these cis expression quantitative trait loci specifically affect the expression of their target gene. In addition, female cortical cells exhibit highly heterogeneous interactions between XIST non-coding RNA and chromosome X, along with diverse spatial organizations of the X chromosomes. MUSIC presents a potent tool for exploration of chromatin architecture and transcription at cellular resolution in complex tissues.