2024-05-14 カリフォルニア大学バークレー校(UCB)
<関連情報>
- https://news.berkeley.edu/2024/05/14/far-from-toxic-lactate-rivals-glucose-as-body-s-major-fuel-after-a-carbohydrate-meal
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s42255-024-00993-1
ヒトにおける腸および全身の食後乳酸シャトルフェーズと食事炭水化物の炭素フロー Enteric and systemic postprandial lactate shuttle phases and dietary carbohydrate carbon flow in humans
Robert G. Leija,Casey C. Curl,Jose A. Arevalo,Adam D. Osmond,Justin J. Duong,Melvin J. Huie,Umesh Masharani & George A. Brooks
Nature Metabolism Published:22 February 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-024-00993-1
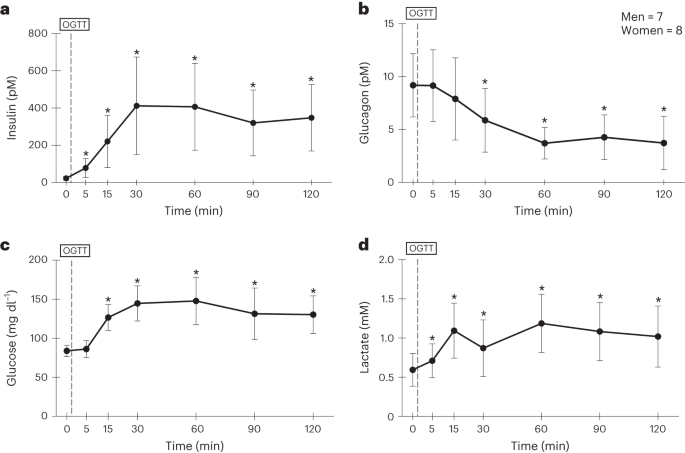
Abstract
Dietary glucose in excess is stored in the liver in the form of glycogen. As opposed to direct conversion of glucose into glycogen, the hypothesis of the postprandial lactate shuttle (PLS) proposes that dietary glucose uptake is metabolized to lactate in the gut, thereby being transferred to the liver for glycogen storage. In the present study, we provide evidence of a PLS in young healthy men and women. Overnight fasted participants underwent an oral glucose tolerance test, and arterialized lactate concentration and rate of appearance were determined. The concentration of lactate in the blood rose before the concentration of glucose, thus providing evidence of an enteric PLS. Secondary increments in the concentration of lactate in the blood and its rate of appearance coincided with those of glucose, which indicates the presence of a larger, secondary, systemic PLS phase driven by hepatic glucose release. The present study challenges the notion that lactate production is the result of hypoxia in skeletal muscles, because our work indicates that glycolysis proceeds to lactate in fully aerobic tissues and dietary carbohydrate is processed via lactate shuttling. Our study proposes that, in humans, lactate is a major vehicle for carbohydrate carbon distribution and metabolism.