2024-06-12 マックス・プランク研究所
<関連情報>
- https://www.mpg.de/22044169/0607-evan-ancient-genomes-reveal-origin-and-spread-of-malaria-150495-x
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07546-2
古代マラリア原虫ゲノムがヒトマラリアの歴史を解明 Ancient Plasmodium genomes shed light on the history of human malaria
Megan Michel,Eirini Skourtanioti,Federica Pierini,Evelyn K. Guevara,Angela Mötsch,Arthur Kocher,Rodrigo Barquera,Raffaela A. Bianco,Selina Carlhoff,Lorenza Coppola Bove,Suzanne Freilich,Karen Giffin,Taylor Hermes,Alina Hiß,Florian Knolle,Elizabeth A. Nelson,Gunnar U. Neumann,Luka Papac,Sandra Penske,Adam B. Rohrlach,Nada Salem,Lena Semerau,Vanessa Villalba-Mouco,Isabelle Abadie,… Johannes Krause
Nature Published:12 June 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07546-2
Abstract
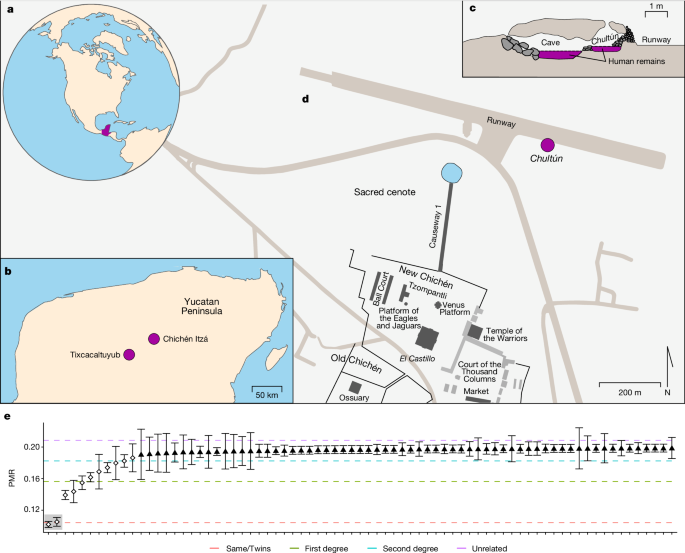
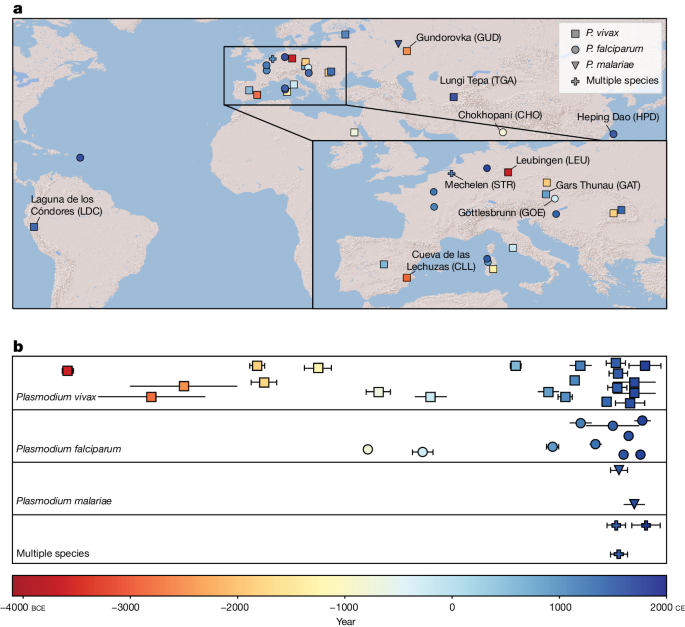
Malaria-causing protozoa of the genus Plasmodium have exerted one of the strongest selective pressures on the human genome, and resistance alleles provide biomolecular footprints that outline the historical reach of these species1. Nevertheless, debate persists over when and how malaria parasites emerged as human pathogens and spread around the globe1,2. To address these questions, we generated high-coverage ancient mitochondrial and nuclear genome-wide data from P. falciparum, P. vivax and P. malariae from 16 countries spanning around 5,500 years of human history. We identified P. vivax and P. falciparum across geographically disparate regions of Eurasia from as early as the fourth and first millennia BCE, respectively; for P. vivax, this evidence pre-dates textual references by several millennia3. Genomic analysis supports distinct disease histories for P. falciparum and P. vivax in the Americas: similarities between now-eliminated European and peri-contact South American strains indicate that European colonizers were the source of American P. vivax, whereas the trans-Atlantic slave trade probably introduced P. falciparum into the Americas. Our data underscore the role of cross-cultural contacts in the dissemination of malaria, laying the biomolecular foundation for future palaeo-epidemiological research into the impact of Plasmodium parasites on human history. Finally, our unexpected discovery of P. falciparum in the high-altitude Himalayas provides a rare case study in which individual mobility can be inferred from infection status, adding to our knowledge of cross-cultural connectivity in the region nearly three millennia ago.