2024-07-11 チャルマース工科大学
<関連情報>
- https://news.cision.com/chalmers/r/blood-fat-profiles-confirm-health-benefits-of-replacing-butter-with-high-quality-plant-oils,c4012145
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-024-03124-1
食事脂肪の質の改善による脂質異常の変化が、心代謝リスク軽減と精密栄養学に役立つ Lipidome changes due to improved dietary fat quality inform cardiometabolic risk reduction and precision nutrition
Fabian Eichelmann,Marcela Prada,Laury Sellem,Kim G. Jackson,Jordi Salas Salvadó,Cristina Razquin Burillo,Ramon Estruch,Michael Friedén,Frederik Rosqvist,Ulf Risérus,Kathryn M. Rexrode,Marta Guasch-Ferré,Qi Sun,Walter C. Willett,Miguel Angel Martinez-Gonzalez,Julie A. Lovegrove,Frank B. Hu,Matthias B. Schulze & Clemens Wittenbecher
Nature Medicine Published:11 July 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-024-03124-1
Abstract
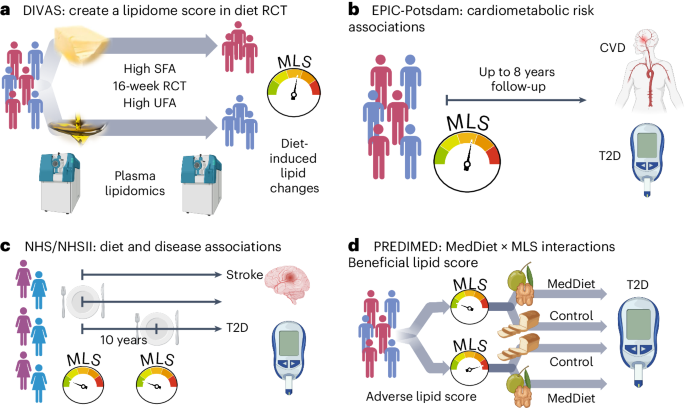
Current cardiometabolic disease prevention guidelines recommend increasing dietary unsaturated fat intake while reducing saturated fats. Here we use lipidomics data from a randomized controlled dietary intervention trial to construct a multilipid score (MLS), summarizing the effects of replacing saturated fat with unsaturated fat on 45 lipid metabolite concentrations. In the EPIC-Potsdam cohort, a difference in the MLS, reflecting better dietary fat quality, was associated with a significant reduction in the incidence of cardiovascular disease (-32%; 95% confidence interval (95% CI): -21% to -42%) and type 2 diabetes (-26%; 95% CI: -15% to -35%). We built a closely correlated simplified score, reduced MLS (rMLS), and observed that beneficial rMLS changes, suggesting improved dietary fat quality over 10 years, were associated with lower diabetes risk (odds ratio per standard deviation of 0.76; 95% CI: 0.59 to 0.98) in the Nurses’ Health Study. Furthermore, in the PREDIMED trial, an olive oil-rich Mediterranean diet intervention primarily reduced diabetes incidence among participants with unfavorable preintervention rMLS levels, suggestive of disturbed lipid metabolism before intervention. Our findings indicate that the effects of dietary fat quality on the lipidome can contribute to a more precise understanding and possible prediction of the health outcomes of specific dietary fat modifications.


