2024-07/30 エディンバラ大学
◆エディンバラ大学と商業パートナーのOptima PartnersおよびBiogenの研究者たちは、UK Biobankの45,000人以上の血液サンプルを機械学習で解析し、病気のリスクを示す特定のタンパク質パターンを特定しました。この手法により、従来のリスク要因よりも高い精度で発症確率を予測できるようになりました。これにより、早期介入や予防の機会が広がる可能性がありますが、実用化にはさらなる研究が必要です。この研究は『Nature Aging』誌に発表され、ウェルカム財団の支援を受けています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.ed.ac.uk/news/2024/ai-insights-predict-disease-a-decade-in-advance
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s43587-024-00655-7#Ack1
英国バイオバンクにおける主要罹患疾患と死亡率の血液タンパク質評価 Blood protein assessment of leading incident diseases and mortality in the UK Biobank
Danni A. Gadd,Robert F. Hillary,Zhana Kuncheva,Tasos Mangelis,Yipeng Cheng,Manju Dissanayake,Romi Admanit,Jake Gagnon,Tinchi Lin,Kyle L. Ferber,Heiko Runz,Biogen Biobank Team,Christopher N. Foley,Riccardo E. Marioni & Benjamin B. Sun
Nature Aging Published:10 July 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s43587-024-00655-7
Abstract
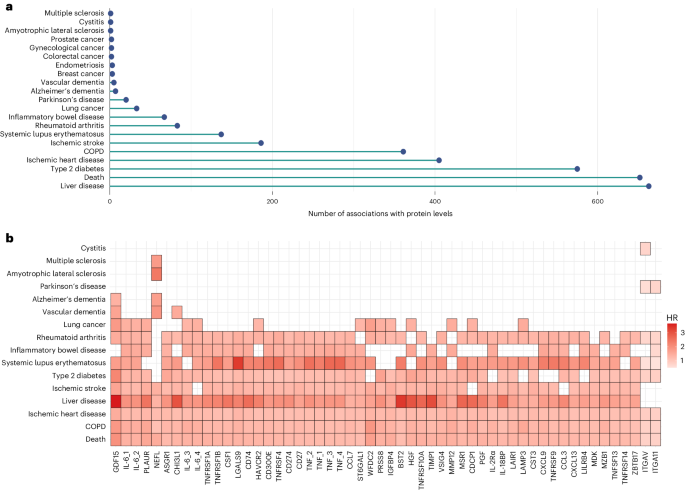
The circulating proteome offers insights into the biological pathways that underlie disease. Here, we test relationships between 1,468 Olink protein levels and the incidence of 23 age-related diseases and mortality in the UK Biobank (n = 47,600). We report 3,209 associations between 963 protein levels and 21 incident outcomes. Next, protein-based scores (ProteinScores) are developed using penalized Cox regression. When applied to test sets, six ProteinScores improve the area under the curve estimates for the 10-year onset of incident outcomes beyond age, sex and a comprehensive set of 24 lifestyle factors, clinically relevant biomarkers and physical measures. Furthermore, the ProteinScore for type 2 diabetes outperforms a polygenic risk score and HbA1c—a clinical marker used to monitor and diagnose type 2 diabetes. The performance of scores using metabolomic and proteomic features is also compared. These data characterize early proteomic contributions to major age-related diseases, demonstrating the value of the plasma proteome for risk stratification.