2024-10-10 デューク大学(Duke)
<関連情報>
- https://pratt.duke.edu/news/optimizing-antibiotic-resistance-inhibitors/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-52711-w
β-ラクタマーゼの自己中心性が抗生物質併用療法の選択ダイナミクスを決定する Private benefit of β-lactamase dictates selection dynamics of combination antibiotic treatment
Helena R. Ma,Helen Z. Xu,Kyeri Kim,Deverick J. Anderson & Lingchong You
Nature Communications Published:27 September 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-52711-w
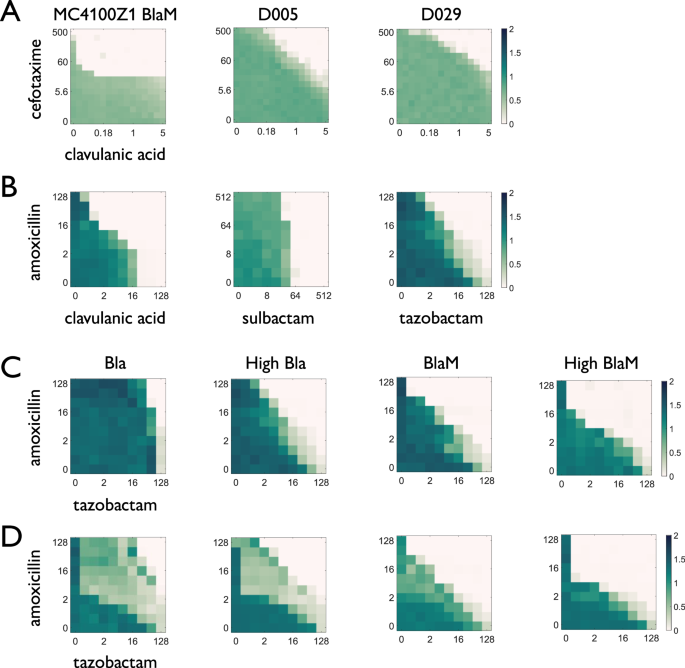
Abstract
β-lactam antibiotics have been prescribed for most bacterial infections since their discovery. However, resistance to β-lactams, mediated by β-lactamase (Bla) enzymes such as extended spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs), has become widespread. Bla inhibitors can restore the efficacy of β-lactams against resistant bacteria, an approach which preserves existing antibiotics despite declining industry investment. However, the effects of combination treatment on selection for β-lactam resistance are not well understood. Bla production confers both private benefits for resistant cells and public benefits which faster-growing sensitive cells can also exploit. These benefits may be differentially impacted by Bla inhibitors, leading to non-intuitive selection dynamics. In this study, we demonstrate strain-to-strain variation in effective combination doses, with complex growth dynamics in mixed populations. Using modeling, we derive a criterion for the selection outcome of combination treatment, dependent on the burden and effective private benefit of Bla production. We then use engineered strains and natural isolates to show that strong private benefits of Bla are associated with increased selection for resistance. Finally, we demonstrate that this parameter can be coarsely estimated using high-throughput phenotyping of clonal populations. Our analysis shows that quantifying the phenotypic responses of bacteria to combination treatment can facilitate resistance-minimizing optimization of treatment.