2024-12-11 マサチューセッツ工科大学(MIT)
<関連情報>
- https://news.mit.edu/2024/noninvasive-imaging-method-can-penetrate-deeper-living-tissue-1211
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adp2438
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-46244-5
生体組織における深く動的な代謝・構造イメージング Deep and dynamic metabolic and structural imaging in living tissues
Kunzan Liu, Honghao Cao, Kasey Shashaty, Li-Yu Yu, […], and Sixian You
Science Advances Published:11 Dec 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adp2438

Abstract
Label-free imaging through two-photon autofluorescence of NAD(P)H allows for nondestructive, high-resolution visualization of cellular activities in living systems. However, its application to thick tissues has been restricted by its limited penetration depth within 300 μm, largely due to light scattering. Here, we demonstrate that the imaging depth for NAD(P)H can be extended to more than 700 μm in living engineered human multicellular microtissues by adopting multimode fiber-based, low repetition rate, high peak power, three-photon excitation of NAD(P)H at 1100 nm. This is achieved by having more than 0.5 megawatts peak power at the band of 1100 ± 25 nm through adaptively modulating multimodal nonlinear pulse propagation with a compact fiber shaper. Moreover, the eightfold increase in pulse energy enables faster imaging of monocyte behaviors in the living multicellular models. These results represent a substantial advance for deep and dynamic imaging of intact living biosystems. The modular design is anticipated to allow wide adoption for demanding imaging applications, including cancer research, immune responses, and tissue engineering.
マルチモーダル非線形パルス伝搬の変調によるスペクトル-時間-空間のカスタマイズ Spectral-temporal-spatial customization via modulating multimodal nonlinear pulse propagation
Tong Qiu,Honghao Cao,Kunzan Liu,Li-Yu Yu,Manuel Levy,Eva Lendaro,Fan Wang & Sixian You
Nature Communications Published:06 March 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46244-5
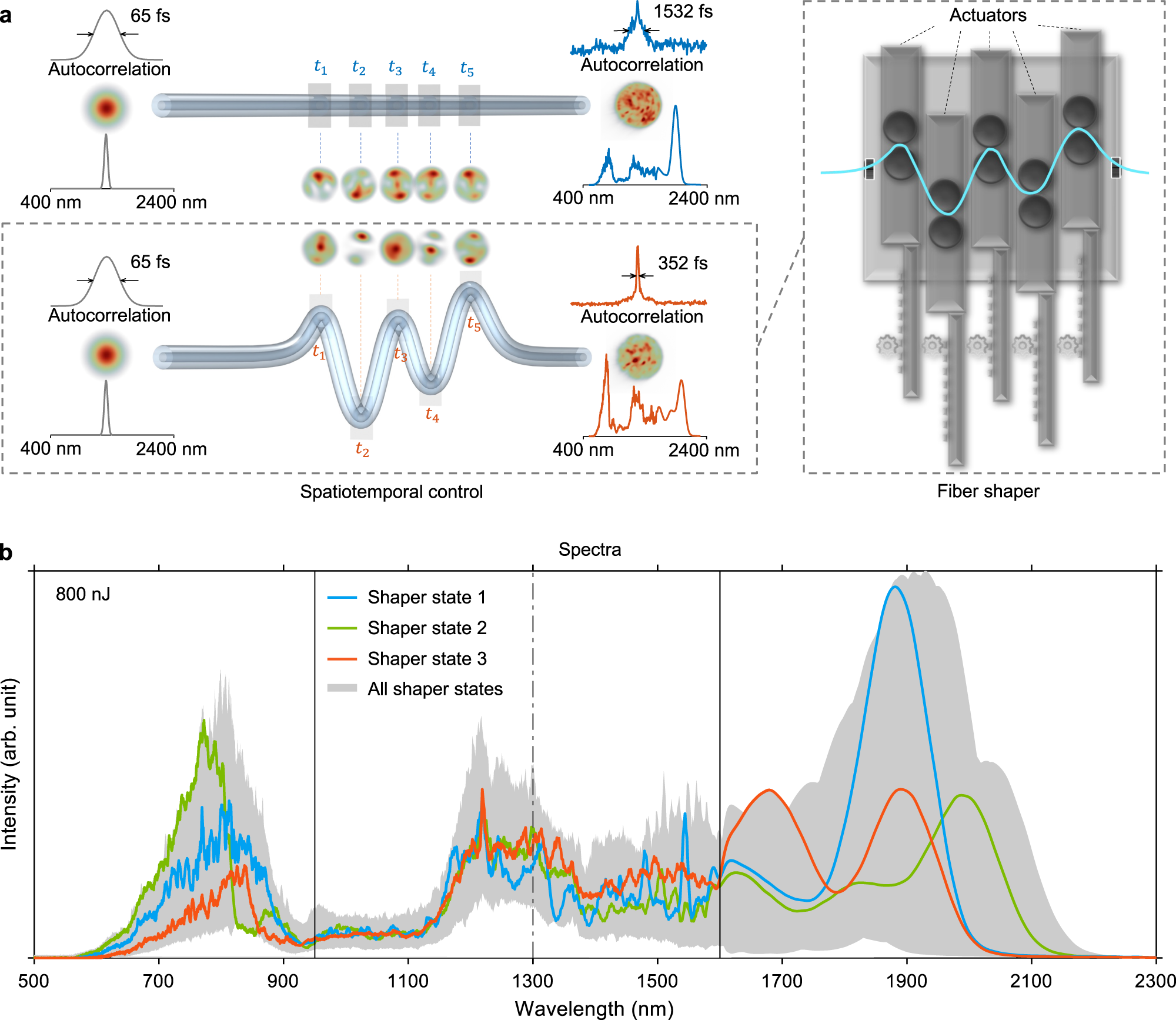
Abstract
Multimode fibers (MMFs) are gaining renewed interest for nonlinear effects due to their high-dimensional spatiotemporal nonlinear dynamics and scalability for high power. High-brightness MMF sources with effective control of the nonlinear processes would offer possibilities in many areas from high-power fiber lasers, to bioimaging and chemical sensing, and to intriguing physics phenomena. Here we present a simple yet effective way of controlling nonlinear effects at high peak power levels. This is achieved by leveraging not only the spatial but also the temporal degrees of freedom during multimodal nonlinear pulse propagation in step-index MMFs, using a programmable fiber shaper that introduces time-dependent disorders. We achieve high tunability in MMF output fields, resulting in a broadband high-peak-power source. Its potential as a nonlinear imaging source is further demonstrated through widely tunable two-photon and three-photon microscopy. These demonstrations provide possibilities for technology advances in nonlinear optics, bioimaging, spectroscopy, optical computing, and material processing.


