2024-12-21 ジョージア工科大学
<関連情報>
- https://research.gatech.edu/special-delivery-nanoparticle-sidesteps-middlemen
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41587-024-02470-2
脂質ナノ粒子を介したアカゲザルのCD34+細胞へのmRNAデリバリー Lipid nanoparticle-mediated mRNA delivery to CD34+ cells in rhesus monkeys
Hyejin Kim,Ryan Zenhausern,Kara Gentry,Liming Lian,Sebastian G. Huayamares,Afsane Radmand,David Loughrey,Ananda R. Podilapu,Marine Z. C. Hatit,Huanzhen Ni,Andrea Li,Aram Shajii,Hannah E. Peck,Keyi Han,Xuanwen Hua,Shu Jia,Michele Martinez,Charles Lee,Philip J. Santangelo,Alice Tarantal & James E. Dahlman
Nature Biotechnology Published:22 November 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-024-02470-2
Abstract
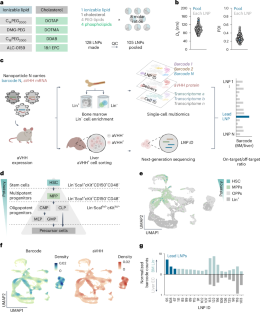
Transplantation of ex vivo engineered hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) can lead to robust clinical responses but carries risks of adverse events from bone marrow mobilization, chemotherapy conditioning and other factors. HSCs have been modified in vivo using lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) decorated with targeting moieties, which increases manufacturing complexity. Here we screen 105 LNPs without targeting ligands for effective homing to the bone marrow in mouse. We report an LNP named LNP67 that delivers mRNA to murine HSCs in vivo, primary human HSCs ex vivo and CD34+ cells in rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) in vivo at doses of 0.25 and 0.4 mg kg-1. Without mobilization and conditioning, LNP67 can mediate delivery of mRNA to HSCs and their progenitor cells (HSPCs), as well as to the liver in rhesus monkeys, without serum cytokine activation. These data support the hypothesis that in vivo delivery to HSCs and HSPCs in nonhuman primates is feasible without targeting ligands.