2025-03-09 カリフォルニア大学リバーサイド校(UCR)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ucr.edu/articles/2025/03/09/longer-sleeker-super-predator-megalodons-true-form
- https://palaeo-electronica.org/content/2025/5450-biology-of-otodus-megalodon
オトダスメガロドンの生物学 Biology of Otodus megalodon
Kenshu Shimada, Ryosuke Motani, Jake J. Wood, Phillip C. Sternes, Taketeru Tomita, Mohamad Bazzi, Alberto Collareta, Joel H. Gayford, Julia Türtscher, Patrick L. Jambura, Jürgen Kriwet, Romain Vullo, Douglas J. Long, Adam P. Summers, John G. Maisey, Charlie Underwood, David J. Ward, Harry M. Maisch IV, Victor J. Perez, Iris Feichtinger, Gavin J.P. Naylor, Joshua K. Moyer, Timothy E. Higham, João Paulo C.B. da Silva, Hugo Bornatowski, Gerardo González-Barba, Michael L. Griffiths, Martin A. Becker, and Mikael Siversson
Palaeontologia Electronica Acceptance: 4 Febuary 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.26879/1502
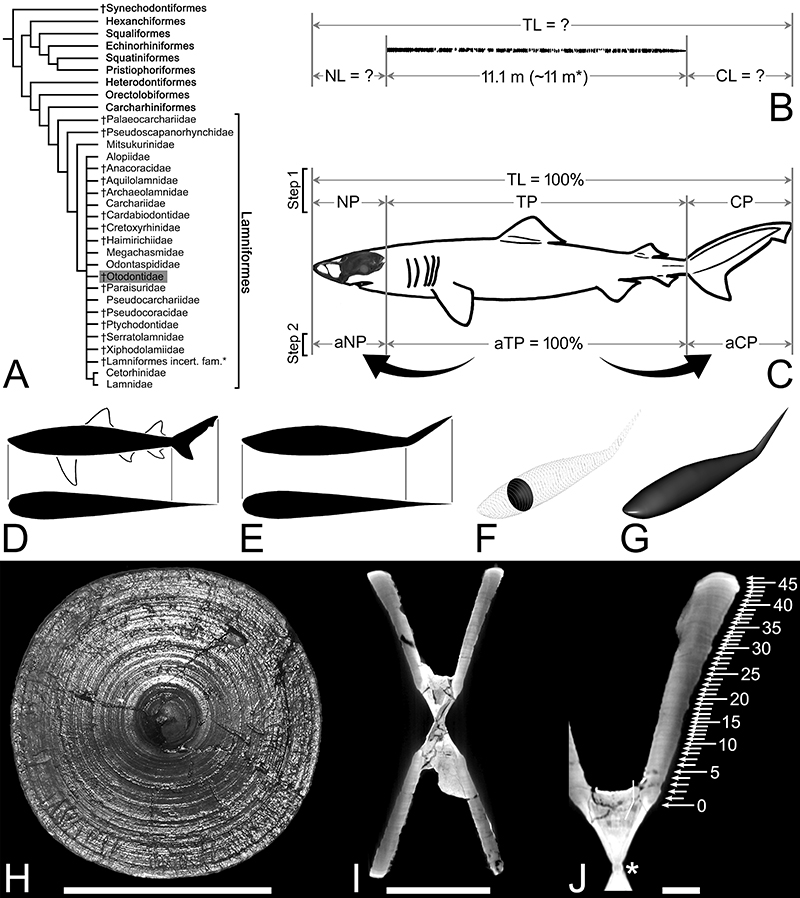
ABSTRACT
Otodus megalodon (Lamniformes: Otodontidae) is an iconic Neogene shark, but the lack of well-preserved skeletons has hampered our understanding of various aspects of its biology. Here, we reassess some of its biological properties using a new approach, based on known vertebral specimens of O. megalodon and 165 species of extinct and extant neoselachian sharks across ten orders. Using the median neurocranial and caudal fin proportions relative to the trunk proportion among non-mitsukurinid/non-alopiid lamniforms, we show that O. megalodon could have had a slender body and possibly reached about 24.3 m in length. Allometric considerations indicate that a stout body plan like the extant white shark (Carcharodon carcharias) for O. megalodon could have incurred excessive hydrodynamic costs, further supporting the interpretation that O. megalodon likely had a slenderer body than C. carcharias. A 24.3-m-long O. megalodon may have weighed around 94 t, with an estimated cruising speed of 2.1–3.5 km h-1. A reanalysis of vertebral growth bands suggests a size at birth of 3.6–3.9 m for O. megalodon, supporting the previous interpretations of its ovoviviparity and embryos’ intrauterine oophagous behavior, but less likely the need for nursery areas. Additional inferred growth patterns corroborated by the known fossil record support the hypothesis that the emergence of C. carcharias during the Early Pliocene is at least partly responsible for the demise of O. megalodon due to competition for resources. These interpretations are working hypotheses expected to serve as reasonable reference points for future studies on the biology of O. megalodon.


