2025-05-01 慶應義塾大学医学部,科学技術振興機構
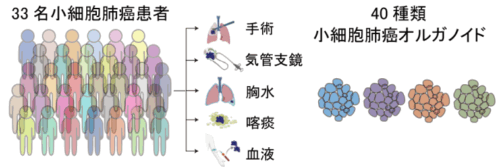
図 1 小細胞肺癌オルガノイドライブラリーの構築
<関連情報>
- https://www.keio.ac.jp/ja/press-releases/2025/5/1/28-166694/
- https://www.keio.ac.jp/ja/press-releases/files/2025/5/1/250501-1.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s43018-025-00945-y
ヒト小細胞肺癌オルガノイドライブラリーを用いた YAP-AP1 経路を介したサブタイプ特異的 IGF-1 依存性の解明 An organoid library unveils subtype-specific IGF-1 dependency via a YAP–AP1 axis in human small cell lung cancer
Takahiro Fukushima,Kazuhiro Togasaki,Junko Hamamoto,Katsura Emoto,Toshiki Ebisudani,Akifumi Mitsuishi,Kai Sugihara,Taro Shinozaki,Masahiko Okada,Ayaka Saito,Hatsuyo Takaoka,Fumimaro Ito,Lisa Shigematsu,Yuki Ohta,Sirirat Takahashi,Mami Matano,Yutaka Kurebayashi,Keiko Ohgino,Takashi Sato,Ichiro Kawada,Keisuke Asakura,Tomoyuki Hishida,Hisao Asamura,Shinnosuke Ikemura,… Toshiro Sato
Nature Cancer Published:30 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-025-00945-y
Abstract
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a devastating disease with limited therapeutic advancements. Although SCLC has recently been classified into four molecular subtypes, subtype-specific therapies are still lacking. Here, we established 40 patient-derived SCLC organoid lines with predominant TP53 and RB1 alterations and rare targetable genetic lesions. Transcriptome profiling divided the SCLC organoids into neuroendocrine (NE)-type SCLC and non-NE-type SCLC, with the latter characterized by YAP1 or POU2F3 expression. NE-type SCLC organoids grew independent of alveolar niche factors, whereas non-NE-type SCLC organoids relied on insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1-driven YAP1 and AP1 activation. Therapeutic targeting of IGF-1, YAP1 and AP1 effectively suppressed the growth of non-NE-type organoids. Co-knockout of TP53 and RB1 in human alveolar cells altered their lineage toward the airway epithelium-like fate and conferred IGF-1 dependency, validating the subtype-phenotype connection. Our SCLC organoid library represents a valuable resource for developing biology-based therapies and has the potential to reshape the drug discovery landscape.