025-04-30 産業技術総合研究所
本研究成果は「Analytical Chemistry」に掲載されました。
<関連情報>
- https://www.aist.go.jp/aist_j/press_release/pr2025/pr20250430/pr20250430.html
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.analchem.5c00646
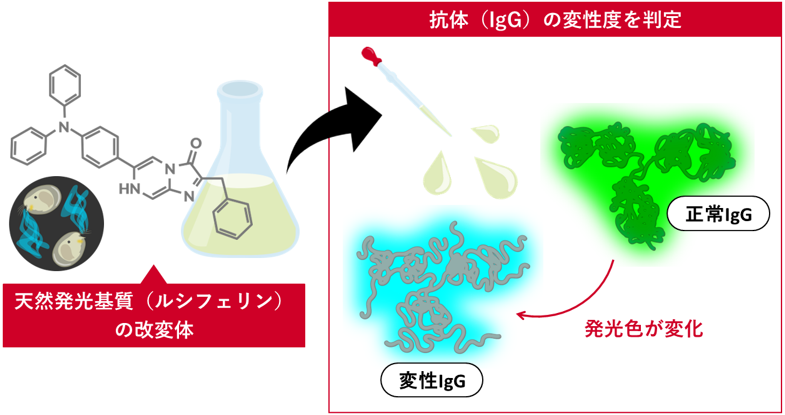
免疫グロブリンG(IgG)中の疑似ルシフェラーゼ活性の発見とIgG変性検出への応用 Discovery of Pseudo-Luciferase Activity in Immunoglobulin G (IgG) and Its Application to the Detection of IgG Denaturation
Ryo Nishihara,Yoshiki Kihara,Eiji Yamamoto,Yoshinori Hirano,Ryoji Kurita
Analytical Chemistry Published: April 30, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5c00646
Abstract
Antibodies are used as diagnostics and as pharmaceuticals, but they are susceptible to degradation at various stages of the manufacturing process. Currently, there is insufficient technology to detect degraded (non-native) antibodies easily and rapidly, despite the degradation of an antibody negatively affecting the product quality, safety, and efficacy. Here, we have developed an assay based on biomolecule-catalyzing chemiluminescence (BCL) in which the native or non-native immunoglobulin G (IgG) itself catalyzes the oxidative luminescent reaction of an imidazopyrazinone-type luciferin and emits different colored light depending on the conformation of the IgG. In this BCL-based assay, the degree of IgG degradation can be detected by simply mixing the luciferin and reading the resulting emission wavelength.


