2025-05-27 マックス・プランク研究所
<関連情報>
- https://www.mpg.de/24789825/gene-scissors-synthetic-crispr-grnas-almost-always-cut
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-59947-0
細胞内のCRISPR切断結果を分離することで、合成gRNA活性と暗号DNA修復を頑健に予測する Robust prediction of synthetic gRNA activity and cryptic DNA repair by disentangling cellular CRISPR cleavage outcomes
Stephan Riesenberg,Philipp Kanis,Rosa Karlic & Tomislav Maricic
Nature Communications Published:21 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-59947-0
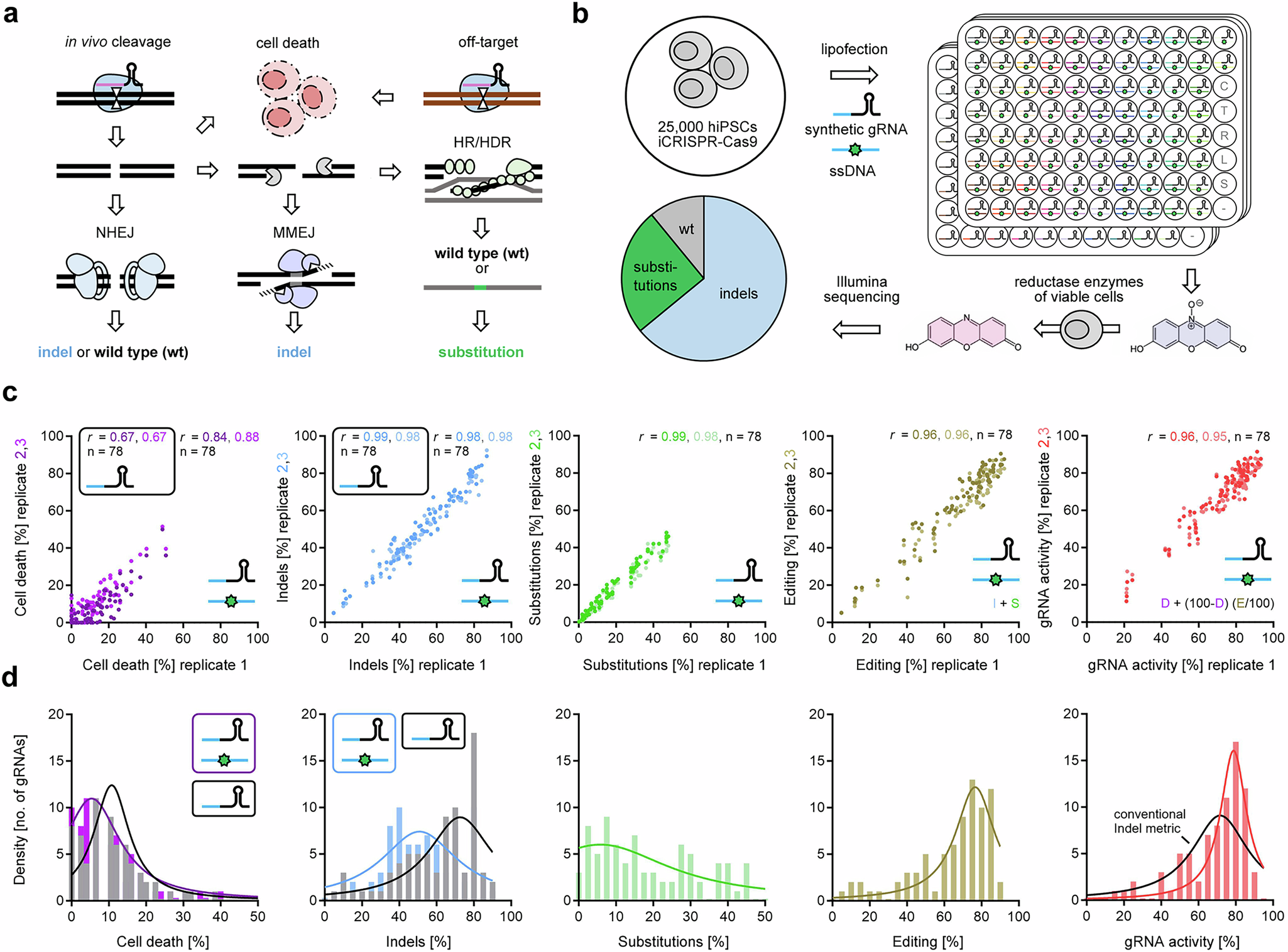
Abstract
The ability to robustly predict guide RNA (gRNA) activity is a long-standing goal for CRISPR applications, as it would reduce the need to pre-screen gRNAs. Quantification of formation of short insertions and deletions (indels) after DNA cleavage by transcribed gRNAs has been typically used to measure and predict gRNA activity. We evaluate the effect of chemically synthesized Cas9 gRNAs on different cellular DNA cleavage outcomes and find that the activity of different gRNAs is largely similar and often underestimated when only indels are scored. We provide a simple linear model that reliably predicts synthetic gRNA activity across cell lines, robustly identifies inefficient gRNAs across different published datasets, and is easily accessible via online genome browser tracks. In addition, we develop a homology-directed repair efficiency prediction tool and show that unintended large-scale repair events are common for Cas9 but not for Cas12a, which may be relevant for safety in gene therapy applications.