2025-06-01 東京大学
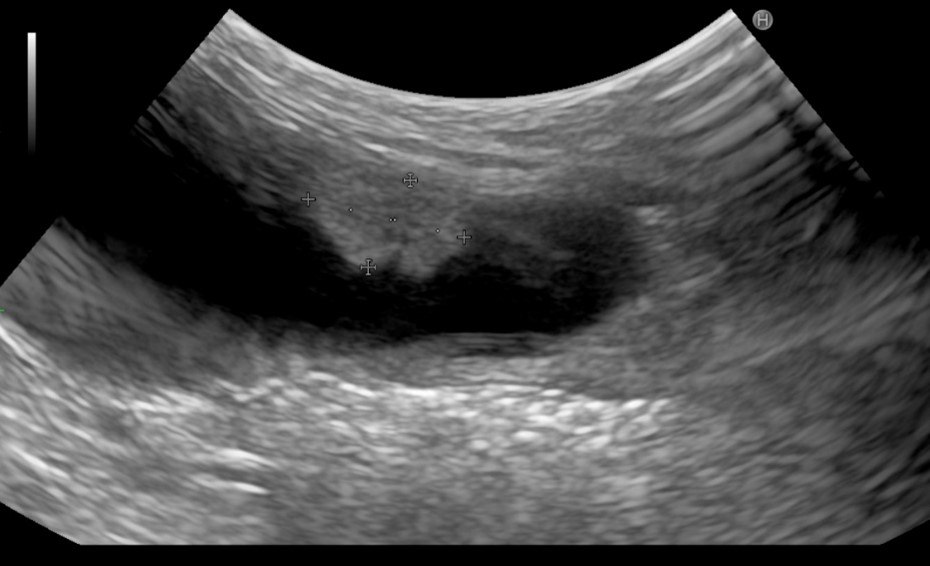
犬の尿路上皮癌の診断時の超音波検査画像
<関連情報>
- https://www.a.u-tokyo.ac.jp/topics/topics_20250601-1.html
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11891803/
犬の膀胱三角部尿路上皮癌における内科的治療を併用した膀胱全摘除術の成績 Outcomes of total cystectomy with medical treatment in canine urothelial carcinoma of the bladder trigone
Yosuke Takahashi, Daiki Kato, Shingo Maeda, Tomoki Motegi, Atsushi Fujita, Yuko Hashimoto, Takayuki Nakagawa, Ryohei Nishimura
The Canadian Veterinary Journal
PMID:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40070938/
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate outcomes and complications in dogs with urothelial carcinoma (UC) of the bladder trigone treated with total cystectomy using uretero-prepuce/vagina/cutaneous anastomosis combined with medical treatment.
Animals: Twenty-one dogs.
Procedure: Total cystectomy was completed as follows: The whole bladder and urethra were removed, and the ureters were anastomosed to the skin in 1 case and to the vagina in 9 cases in females. The entire bladder, prostate, urethra, and penis were removed, and the ureters were anastomosed to the prepuce in 11 males. Medical treatments were administered to all dogs after surgery.
Results: Short-term surgical complications included diarrhea (16 dogs), acute kidney injury (2 dogs), and dehiscence of the ureterovaginal anastomosis (3 dogs). Long-term surgical and medical complications included pyelonephritis (11 dogs) and chronic kidney disease (5 dogs). In the survival analysis, median survival time from the initial diagnosis in all cases was 481 d, which was longer than the previously reported median survival time in dogs with UC involving the trigone.
Conclusion and clinical relevance: Total cystectomy combined with medical treatment prolonged overall survival compared with medical, surgical, or stenting procedures in dogs with UC involving the trigone.
Copyright and/or publishing rights held by the Canadian Veterinary Medical Association.