2025-06-05 ヘルムホルツドイツ研究センター協会
<関連情報>
- https://www.dkfz.de/en/news/press-releases/detail/darmkrebs-screening-per-smartphone
- https://www.cghjournal.org/article/S1542-3565(25)00423-9/pdf
大腸がん検診におけるスマートフォンを用いた検便の性能:集団ベースの研究 Performance of a smartphone-based stool test for use in colorectal cancer screening: population-based study
Michael Hoffmeister, Teresa Seum, Leopold Ludwig, Hermann Brenner
Clin Gastroenterol Hep Accepted Date: 2 April 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2025.04.027
Abstract
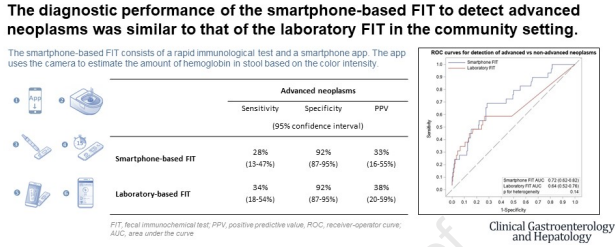
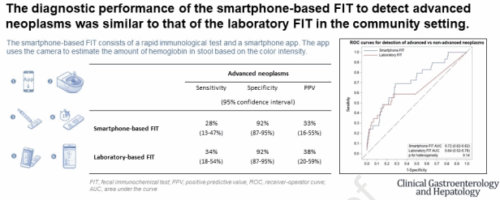
Background and aims: Non-invasive colorectal cancer (CRC) screening bears high potential for increasing participation if implemented in a straightforward way. We have evaluated the feasibility and diagnostic performance of a smartphone-based fecal immunochemical test (FIT) for CRC screening and compared its performance of with a laboratory-based FIT.
Methods: Individuals scheduled for a screening colonoscopy in gastroenterology practices in Southern Germany enrolled into the BLITZ study between 2021 and 2023 were offered a smartphone-based FIT and a laboratory FIT. The smartphone-based FIT consists of a rapid test and a smartphone app. The app quantitatively evaluates the result of the rapid test using the smartphone camera.. The feasibility of the smartphone-based FIT was evaluated in a self-administered questionnaire. The comparative performance of the two FITs was evaluated by sensitivity, specificity and receiver-operator curve (ROC) measures.
Results: Of 654 study participants who were offered both a smartphone-based FIT in addition to the laboratory FIT, 361 (55%) made use of the smartphone-based FIT, 274 (76%) of those had a valid smartphone-based FIT, and 643 (98%) used the laboratory FIT. Overall 89% considered the smartphone-based FIT as a useful alternative offer to the laboratory FIT. The reasons why the smartphone-based FIT was not used were mostly technical (app- or smartphone-related, 47%), or reflecting more general concerns or attitudes towards such a test (44%). The smartphone-based FIT showed a sensitivity for advanced neoplasms (28%, 95% confidence interval 13-47%) similar to the laboratory FIT (34%, 18-54%) at an identical specificity (92%, 87-95%).
Conclusion: The smartphone-based FIT could serve as an alternative in addition to currently offered laboratory FITs. drks.de, DRKS00008737.
Keywords: FIT; colonoscopy; digital prevention; early detection; self-test.