2025-06-10 聖マリアンナ医科大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.marianna-u.ac.jp/houjin/today/20250610_01/
- https://www.marianna-u.ac.jp/houjin/today/20250610_01/01.pdf
- https://insight.jci.org/articles/view/184530
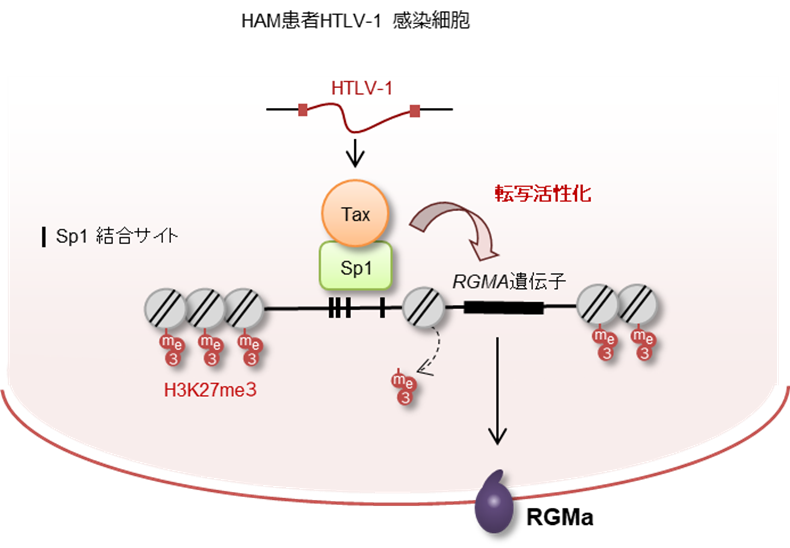
ウイルス誘導性RGMa発現がHTLV-1関連脊髄症における神経変性を促進する Virus-induced RGMa expression drives neurodegeneration in HTLV-1–associated myelopathy
Natsumi Araya,Makoto Yamagishi,Makoto Nakashima,Naomi Asahara,Kazuhiro Kiyohara,Satoko Aratani,Naoko Yagishita,Erika Horibe,Izumi Ishizaki,Toshiki Watanabe,Tomoo Sato,Kaoru Uchimaru, and Yoshihisa Yamano
JCI Insight Published: April 30, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.184530
Abstract
Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1–associated (HTLV-1–associated) myelopathy (HAM, also known as tropical spastic paraparesis) is a rare neurodegenerative disease with largely elusive molecular mechanisms, impeding targeted therapeutic advancements. This study aimed to identify the critical molecule responsible for neuronal damage in HAM, its source, and the regulatory mechanisms controlling its expression. Utilizing patient-derived cells and established cell lines, we discovered that HTLV-1 Tax, in conjunction with specificity protein 1 (Sp1), enhanced the expression of repulsive guidance molecule A (RGMa), a protein known to contribute to neuronal damage. RGMa expression was specifically upregulated in HTLV-1–infected cells from patients with HAM, particularly in those expressing HTLV-1 Tax. Furthermore, in CD4+ cells from patients with HAM, the level of H3K27me3 methylation upstream of the RGMA gene locus was reduced, making RGMA more prone to constitutive expression. We demonstrated that HTLV-1–infected cells in HAM inflict neuronal damage via RGMa. Crucially, the neutralizing antibody against RGMa, unasnemab (MT-3921), effectively mitigated this damage in a dose-responsive manner, highlighting RGMa’s pivotal role in neuronal damage and its potential as a therapeutic target for alleviating neuronal damage in HAM.