2025-06-13 東京大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/focus/ja/press/z0406_00006.html
- https://www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/content/400265738.pdf
- https://www.thelancet.com/journals/ebiom/article/PIIS2352-3964(25)00238-5/fulltext
SARS-CoV-2オミクロンXBB.1.5受容体結合ドメインをコードするmRNAワクチンがJN.1変異体からマウスを守る An mRNA vaccine encoding the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron XBB.1.5 receptor-binding domain protects mice from the JN.1 variant
Ryuta Uraki ∙ Maki Kiso ∙ Mutsumi Ito ∙ Seiya Yamayoshi ∙ Peter Halfmann ∙ Shilpi Jain ∙ et al.
eBioMedicine Published: June 6, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105794
Summary
Background
The SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2.86 variant and its descendant lineages, including JN.1, are rapidly spreading globally. We developed mRNA encoding the SARS-CoV-2 RBD derived from XBB.1.5 (XBB.1.5-type LNP-mRNA-RBD), in line with WHO recommendations. Many individuals have acquired immunity specific to the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 strain or early Omicron variants, such as BA.1, BA.2, or BA.5, through natural infection and/or vaccination. However, the efficacy of XBB.1.5-type LNP-mRNA-RBD boost vaccination against a clinical isolate of JN.1 remains uncertain.
Methods
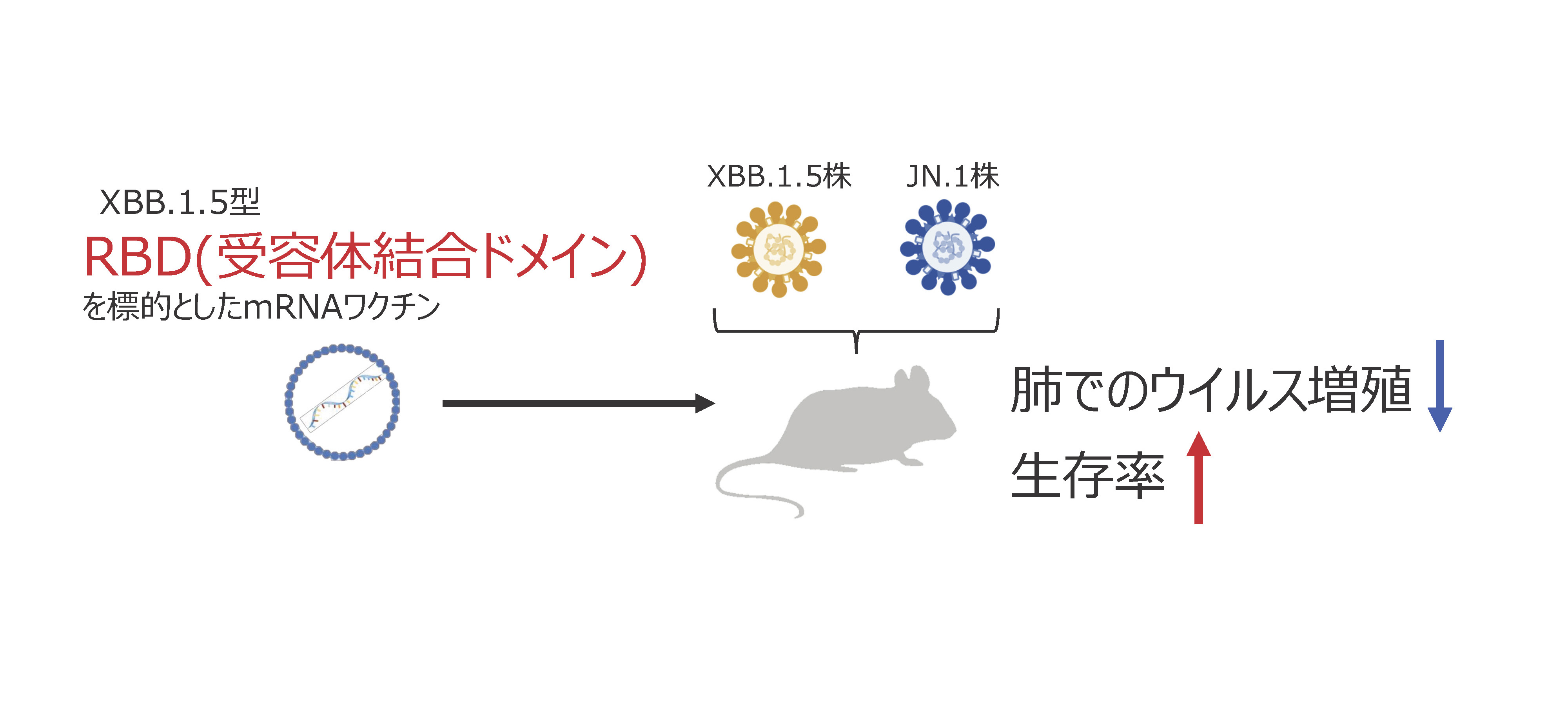
In this study, we used a small amount of LNP-mRNA-RBD as a prime dose compared with a booster shot to mimic the waning immunity against the ancestral and BA.4/5 strains. We immunised female mice with XBB.1.5-type LNP-mRNA-RBD as a booster vaccine and examined the cellular and humoural responses as well as the protective efficacy against a JN.1 variant.
Findings
We found that immunisation of mice with the XBB.1.5-type LNP-mRNA-RBD as a booster shot induced XBB.1.5-specific neutralising activity and T cell responses. Moreover, immunisation with a bivalent vaccine consisting of the ancestral-type and BA.4/5-type LNP-mRNA-RBD as the primary dose followed by XBB.1.5-type LNP-mRNA-RBD boosting induced enhanced levels of cross-reactive antibodies against the JN.1 strain, compared to using the ancestral-type vaccine as the primary dose. In addition, we found that a booster shot of LNP-mRNA-RBD based on the XBB.1.5 strain reduced the viral burden in the respiratory organs after JN.1 challenge.
Interpretation
Our findings suggest that XBB.1.5-type LNP-mRNA-RBD is effective against antigenically distinct JN.1 infection.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Japan Program for Infectious Diseases Research and Infrastructure (JP25wm0125002), the Japan Initiative for World-leading Vaccine Research and Development Centers (JP253fa627001), and the Vaccine Development project (JP21nf0101625) from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, and the National Institutes of Allergy and Infectious DiseasesCenter for Research on Influenza Pathogenesis and Transmission (CRIPT) (75N93021C00014).