2025-07-28カロリンスカ研究所(KI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ki.se/healthy-diet-can-slow-down-chronic-diseases-in-older-people
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s43587-025-00929-8
高齢者の食事パターンと多疾患併発の加速化 Dietary patterns and accelerated multimorbidity in older adults
David Abbad-Gomez,Adrián Carballo-Casla,Giorgi Beridze,Esther Lopez-Garcia,Fernando Rodríguez-Artalejo,Maria Sala,Mercè Comas,Davide Liborio Vetrano & Amaia Calderón-Larrañaga
Nature Aging Published:28 July 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s43587-025-00929-8
Abstract
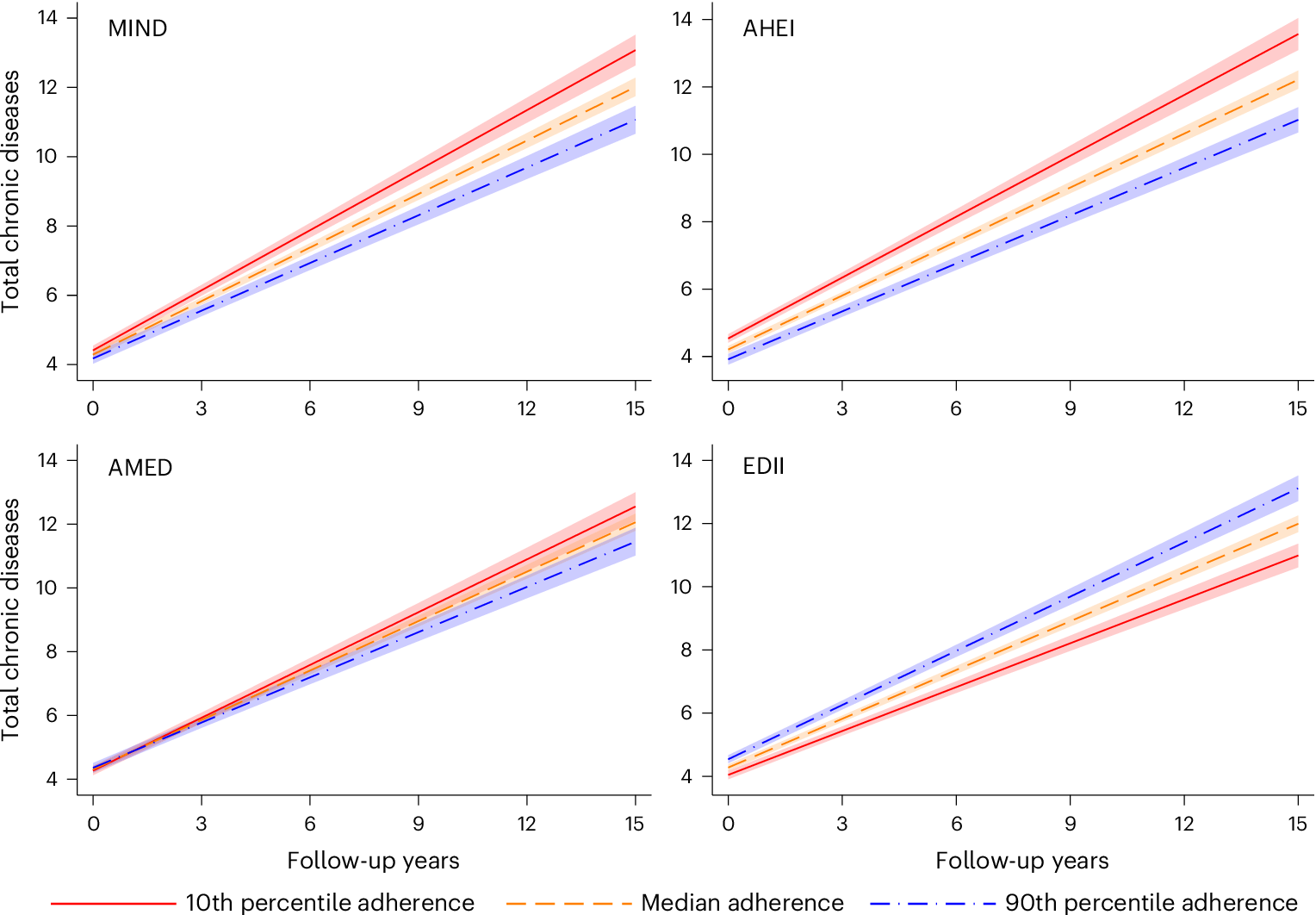
Diet could influence disease development and shape multimorbidity trajectories. Here we examined how four dietary patterns relate to 15-year multimorbidity accumulation in 2,473 community-dwelling older adults from the Swedish SNAC-K cohort. Multimorbidity was operationalized as the total number of chronic conditions and grouped into three organ systems. Higher adherence to the Mediterranean-DASH Diet Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay, the Alternative Healthy Eating Index and the Alternative Mediterranean Diet was inversely associated with the annual rate of total chronic disease accumulation (β coefficient (95% confidence interval) per 1-s.d. increment: -0.049 (-0.065 to -0.032), -0.051 (-0.068 to -0.035) and -0.031 (-0.048 to -0.014), respectively), whereas higher adherence to the Empirical Dietary Inflammatory Index was associated with a faster rate of accumulation (0.053 (0.035–0.071)). Similar associations were observed for cardiovascular and neuropsychiatric diseases but not for musculoskeletal diseases. Some associations varied by sex and age. Our findings support diet quality as a modifiable risk factor for multimorbidity progression in older adults, with possible implications for dietary guidelines, public health strategies and clinical practice.