2025-07-29 京都大学
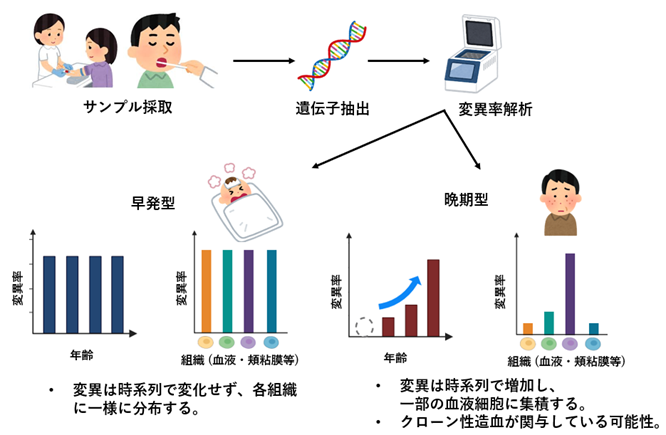
本研究の概要図
<関連情報>
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/ja/research-news/2025-07-29-2
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/sites/default/files/2025-07/web_2507_Kato-fcc2bdb442b71e2665e23bec14688319.pdf
- https://acrjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/art.43329
クリオピリン関連周期熱症候群における体細胞モザイクおよびクローン性造血の経時的解析 Longitudinal Analysis of Somatic Mosaicism and Clonal Hematopoiesis in Cryopyrin-Associated Periodic Syndrome
Kentaro Kato MD, Yoshitaka Honda MD PhD, Takashi Kamatani MD PhD, Kosaku Murakami MD PhD, Masaki Shimizu MD PhD, Toshihiko Komai MD PhD, Hiroko Kanda MD PhD …
Arthritis & Rheumatology Published: 22 July 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/art.43329
Abstract
Objective
Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome (CAPS) is an autoinflammatory disease caused by gain-of-function mutations in NLRP3. Although somatic NLRP3 mosaicism is increasingly recognized, it remains unclear how variant allele frequency (VAF) changes over time and whether disease onset age reflects differences in somatic mutation dynamics. This study aimed to analyze the longitudinal VAF trends and their correlation with clonal hematopoiesis (CH) in patients with CAPS mosaicism.
Methods
We analyzed NLRP3 VAF in blood and various tissues, including dried umbilical cord (DUC) using digital PCR and deep amplicon sequencing. Whole-exome and single-cell genome sequencing were performed to evaluate CH-related mutations.
Results
We included 15 patients with VAFs of 4.3% to 34.9%. In the 12 early-onset cases, VAFs were generally consistent across various tissues and did not increase over time, including the DUC. Conversely, in the three late-onset cases, VAFs were particularly high in myeloid cells. Notably, in one late-onset case, no mutations were detected in DUC. After disease onset, VAFs exhibited 2.9%-to-10.6% and 6.2%-to-16.4% increase in the whole blood and neutrophils over 6.4 and 4.4 years, respectively, showing a clonal expansion of NLRP3-mutant cells. Single-cell genome sequencing revealed frequent co-occurrence of NLRP3 and TET2 mutations in the same cells, with a gradual increase in both VAFs over 3 years, in one late-onset case.
Conclusion
In early-onset cases, the VAFs were comparable across various tissues and did not increase over time. Mutations in late-onset cases were enriched in myeloid cells, and VAFs were increased, suggesting a link to CH.