2025-08-01 コペンハーゲン大学(UCPH)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ku.dk/all_news/2025/07/microbiome-breakthrough-gut-bacterium-may-hold-key-to-future-treatments-for-widespread-chronic-diseases/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-025-02064-x
ヒト腸内における一般的な細菌によって合成されるポリペプチドがげっ歯類の代謝を改善する Polypeptides synthesized by common bacteria in the human gut improve rodent metabolism
Yong Fan,Liwei Lyu,Ruben Vazquez-Uribe,Wanliang Zhang,Mareike Bongers,Andreas Koulouktsis,Mengliu Yang,Vita Sereika-Bejder,Tulika Arora,Evelina Stankevic,Jeremy Armetta,Franziska Zosel,Charlotta D. de la Cour,Lotte Simonsen,Alina Kulakova,Michael Wierer,Pernille Harris,Joachim Gæde,Peter Rossing,Filip K. Knop,Tune H. Pers,Tue Haldor Hansen,Trine Nielsen,Ling Li,… Oluf Pedersen
Nature Microbiology Published:31 July 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-025-02064-x
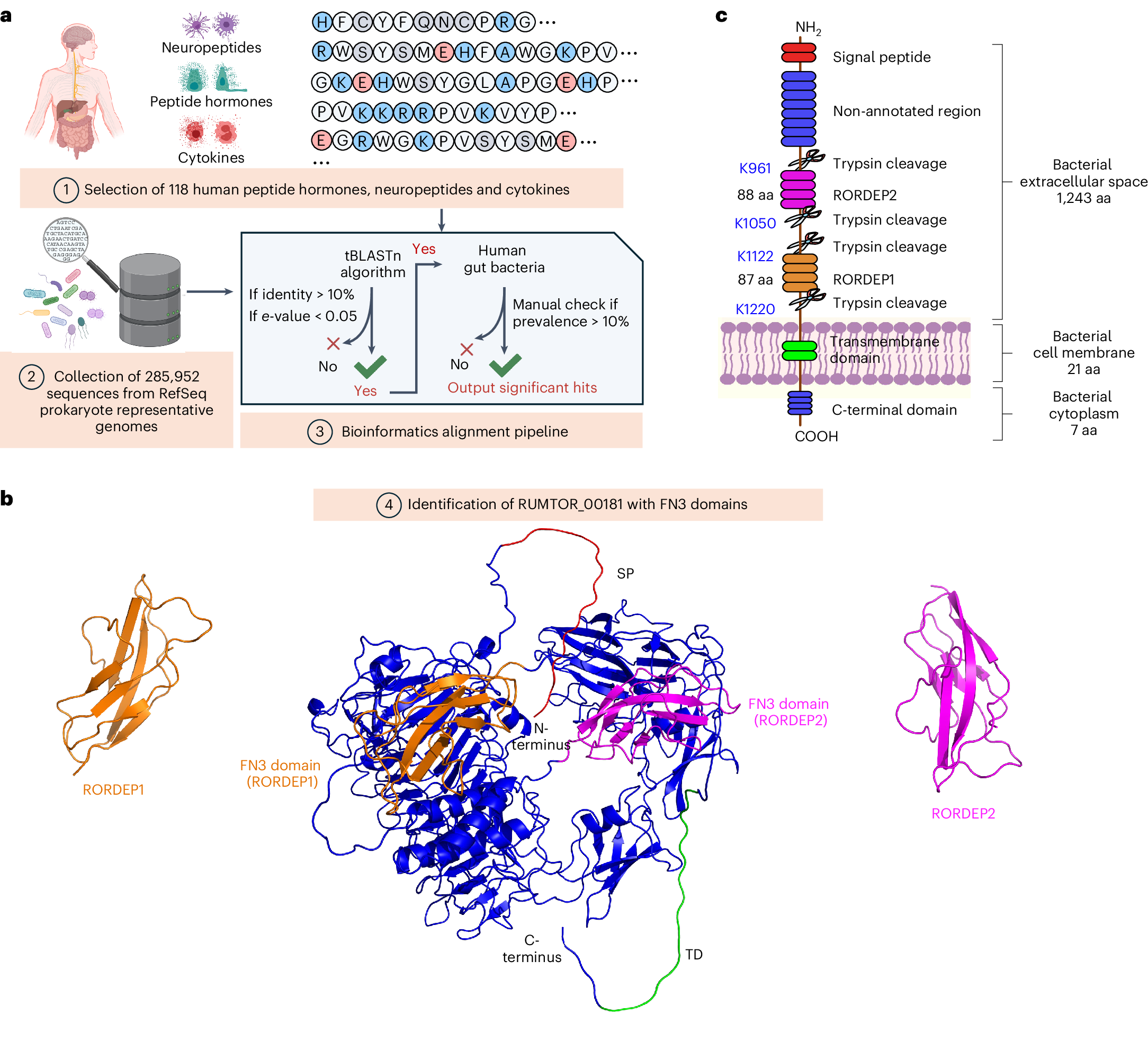
Abstract
The human gut microbiota has the potential to synthesize proteins that may influence host metabolism. Here we report two polypeptides, RUMTOR-derived peptide (RORDEP) 1 and RORDEP2, circulating in human blood and synthesized by specific strains of gut commensal Ruminococcus torques that correlate inversely with adiposity in humans. Oral gavage with RORDEP-expressing strains improved glucose tolerance, increased bone density and reduced fat mass with an enhanced expression of genes and proteins involved in thermogenesis and lipolysis in lean mice on a high-fat diet and diet-induced obese mice. Recombinant RORDEP1 given to rats intraperitoneally decreased plasma gastric inhibitory polypeptide but increased glucagon-like peptide 1, peptide YY and insulin. Intestinal delivery of recombinant RORDEP1 to rats potentiated insulin-mediated inhibition of hepatic glucose production by downregulating genes and proteins controlling liver gluconeogenesis, glycogenolysis and lipogenesis but upregulating those involved in insulin signalling, glycogenesis and glycolysis. These preclinical findings warrant the exploration of RORDEPs for the prevention and treatment of human metabolic disorders.


