2025-09-03 オックスフォード大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.ox.ac.uk/news/2025-09-03-new-shelf-immunotherapy-shows-promise-treating-high-risk-childhood-leukaemia
- https://ashpublications.org/blood/article/doi/10.1182/blood.2025029302/547084/Off-the-shelf-dual-CAR-iNKT-cell-immunotherapy
既製デュアルCAR-iNKT細胞免疫療法が髄質性・軟髄膜性高リスクKMT2A再構成白血病を根絶 Off-the-shelf dual CAR-iNKT cell immunotherapy eradicates medullary and leptomeningeal high-risk KMT2A-rearranged leukemia
Hongwei Ren,Natalina Elliott,Bryan Lye,Mohammad Umer Sharif Shohan,Joe Wilson Cross,Lucy May Field,Kanagaraju Ponnusamy,Siobhan Rice,Thomas Jackson,Ilia Leontari,Nouhad El Ouazzani,Rebecca Thomas,Sarah Inglott,Jack Bartram,Owen Smith, Professor,Jonathan Bond,Irene Roberts,Christina Halsey,Rachael Bashford-Rogers,Thomas A Milne,Anindita Roy,Anastasios Karadimitris
Blood Published:September 3, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2025029302
Key Points
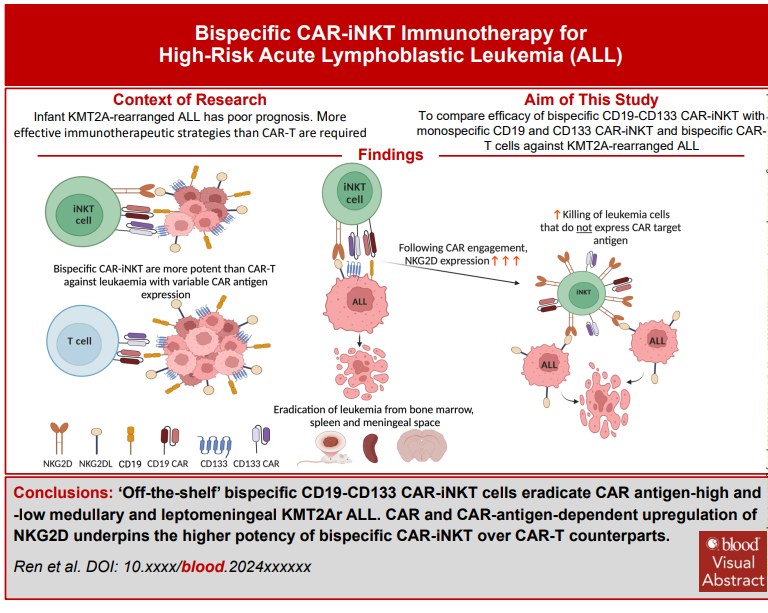
- ‘Off-the-shelf’ bispecific CD133-CD19 CAR-iNKT cells eradicate CAR antigen-high and -low medullary and leptomeningeal KMT2Ar ALL
- CAR and CAR-antigen-dependent upregulation of NKG2D underpins the higher potency of bispecific CAR-iNKT over CAR-T counterparts
Current therapies, including autologous CAR-T immunotherapy, fail to cure half of infants with KMT2A-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemia (KMT2Ar-ALL), a disease characterized by frequent central nervous system involvement, poor treatment response, early relapse and lineage switching. More effective treatment strategies, including the availability of ‘off-the-shelf’ immunotherapies is particularly relevant in infants. PROM1/CD133 is a direct target of KMT2A-fusion oncoproteins and is expressed on leukemic cells. Allogeneic iNKT cells, ‘innately’ more powerful effectors than T cells can be deployed ‘off-the-shelf’ without risk of acute graft-versus-host disease. Here, we equip iNKT with CD19- and/or CD133-targeting CARs and investigate their anti-leukaemia activity against KMT2Ar-ALL in relevant in vitro and in vivo models. Compared to mono-specific counterparts and dual, bi-specific CAR-T, bi-specific CD19-CD133 CAR-iNKT have a more potent anti-leukemia activity, effectively targeting both CAR antigen-high and -low leukemia. Bi-specific CAR-iNKT eradicate medullary and, notably, leptomeningeal leukemia and induce sustained remissions without discernible hematologic toxicity. Mechanistically, the more potent anti-leukemia effect of CAR-iNKT over CAR-T cells is mediated by a pronounced CAR- and CAR antigen-dependent upregulation of the innate activating receptor NKG2D on CAR-iNKT and its engagement by its corresponding ligands on KMT2Ar-ALL cells. This ensures effective leukemia targeting even with downregulation of CD133 or CD19. Thus, by engaging with two different types of leukemia-associated antigens i.e., CAR antigens and NKG2D ligands, CAR-iNKT provide a powerful platform for the treatment of KMT2Ar-ALL. This approach can be readily adapted for other high-risk malignancies, including those with otherwise difficult to target leptomeningeal involvement.


00213-5/asset/b1687a8a-87b6-4c93-8371-fbaf48cc56d0/main.assets/gr1.jpg)