2025-09-04 京都大学
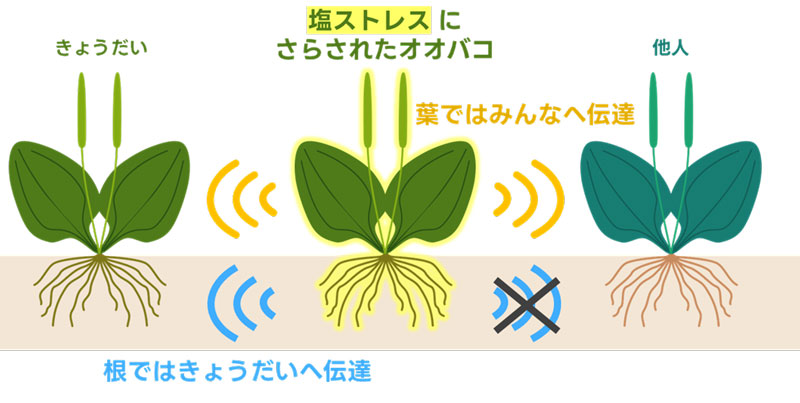
研究成果の概念図
<関連情報>
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/ja/research-news/2025-09-04-3
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/sites/default/files/2025-09/web_2509_Yamawo-6f06cc8069a0287863fc92327c89df53.pdf
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/15592324.2025.2542560
塩ストレスに対する地上部と地下部の統合的な相互刺激 Integrated above- and below-ground interplant cueing of salt stress
Kai Ito,Haruna Ohsaki,Ariel Novoplansky,Shun K. Hirota&Akira Yamawo
Plant Signaling & Behavior Published:12 Aug 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2025.2542560
ABSTRACT
Neighboring plants exchange adaptive information related to their genetic identity, stress experiences, and reproductive state. Here, we tested the possibility that Plantago asiatica plants utilize both above- and below-ground communication to differentially respond to stress cues perceived from neighbors with variable genetic identities. Stress response was observed by recording stomatal aperture in stressed plants and their neighbors while restricting interplant communication to either root or shoot cueing. Split-root plants were planted in triplets at equidistant intervals. Half of the roots of the central plant were subjected to salt stress, while the other half shared its rooting volume with the roots of an unstressed neighboring plant on one side, and its headspace with another unstressed neighbor on the other side. Sixty minutes after the onset of salt stress, soil-sharing neighbors had a larger proportion of closed stomata when the stressed plant was genetically closer (sibling [SB] or from a near population [NP]) than from a more remote population (FP). In contrast, aboveground stress cueing was equally effective regardless of the genetic relatedness of the neighboring plants. The findings demonstrate for the first time a concurrent utilization of both specific and nonspecific interplant stress cueing. The results call for further investigation into the adaptive implications of these communication modes on the survival and performance of P. asiatica under variable environmental scenarios.


