2025-09-11 学習院大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.univ.gakushuin.ac.jp/about/press/31107.html
- https://www.univ.gakushuin.ac.jp/about/press/docs/20250911pressrelease.pdf
- https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/aging-neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2025.1571429/full
アルツハイマー病早期発見のための仮想現実ナビゲーション
Virtual reality navigation for the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease
Sayuri Shima,Reiko Ohdake,Yasuaki Mizutani,Harutsugu Tatebe,Riki Koike,Atsushi Kasai,Epifanio Bagarinao,Kazuya Kawabata,Akihiro Ueda,Mizuki Ito,Junichi Hata,Shinsuke Ishigaki,Junichiro Yoshimoto,Hiroshi Toyama,Takahiko Tokuda,Akihiko Takashima,Hirohisa Watanabe
Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience Published:20 August 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2025.1571429
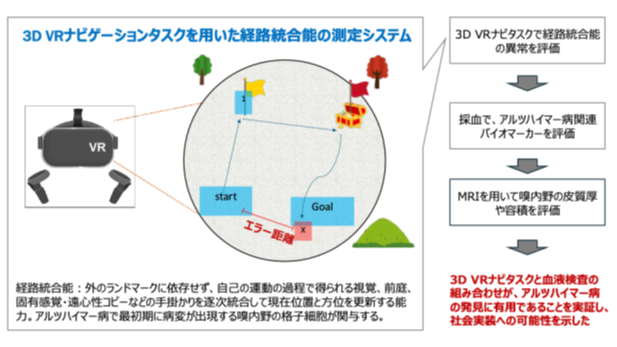
Objective: The development of non-invasive clinical diagnostics is paramount for the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Neurofibrillary tangles in AD originate from the entorhinal cortex, a cortical memory area that mediates navigation via path integration (PI). Here, we studied correlations between PI errors and levels of a range of AD biomarkers using a 3D virtual reality navigation system to explore PI as a non-invasive surrogate marker for early detection.
Methods: We examined 111 healthy adults for PI using a head-mounted 3D VR system, AD-related plasma biomarkers (GFAP, NfL, Aβ40, Aβ42, and p-tau181), Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) genotype, and demographic and cognitive assessments. Covariance of PI and AD biomarkers was assessed statistically, including tests for multivariate linear regression, logistic regression, and predictor importance ranking using machine learning, to identify predictive relationships for PI errors.
Results: We found significant positive correlations between PI errors with age and plasma GFAP, p-tau181, and NfL levels. Multivariate analysis identified significant correlations of plasma GFAP (t-value = 2.16, p = 0.0332) and p-tau181 (t-value = 2.53, p = 0.0128) with PI errors. Predictor importance ranking using machine learning and receiver operating characteristic curves identified plasma p-tau181 as the most significant predictor of PI. ApoE genotype and plasma p-tau181 showed positive and negative PI associations (ApoE: coefficient = 0.650, p = 0.037; p-tau181: coefficient = -0.899, p = 0.041). EC thickness exhibited negative correlations with age, mean PI errors, and GFAP, NfL, and p-tau181; however, none of these associations remained significant after adjusting for age in linear regression analyses.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that PI quantified by 3D VR navigation systems may be useful as a surrogate diagnostic tool for the detection of early AD pathophysiology. The hierarchical application of 3D VR PI and plasma p-tau181, in particular, may be an effective combinatorial biomarker for early AD neurodegeneration. These findings advance the application of non-invasive diagnostic tools for early testing and monitoring of AD, paving the way for timely therapeutic interventions and improved epidemiological patient outcomes.


