2025-09-12 パシフィック・ノースウェスト国立研究所(PNNL)
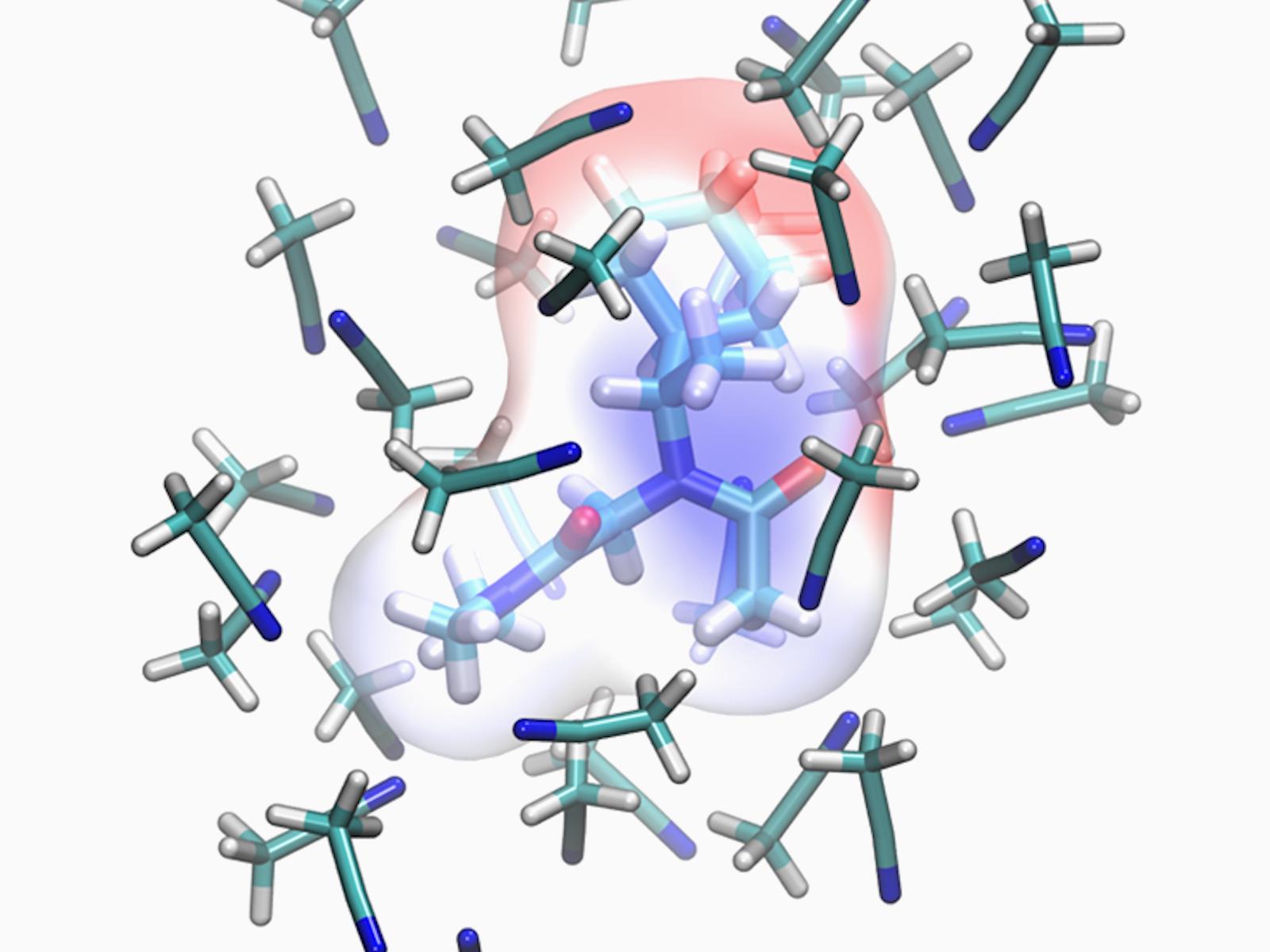
Electrostatic potential mapped on the van der Waals surface of the R57 peptoid monomer in acetonitrile, highlighting the solvent-dependent charge distribution used in STEPs-SOL.
(Image by Marcel Baer | Pacific Northwest National Laboratory)
<関連情報>
- https://www.pnnl.gov/publications/accounting-solvent-polarization-improves-conformational-predictions-peptoid-force
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jpcb.5c02834
溶媒効果を考慮したペプトイド力場パラメータ化:STEPs-SOL STEPs-SOL, a Peptoid Force Field Parameterization to Include Solvent Effects
Yasmene W. Elhady,Bradley S. Harris,Christopher J. Mundy,and Marcel D. Baer
The Journal of Physical Chemistry B Published: June 3, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcb.5c02834
Abstract
As peptoids (N-substituted glycines) continue to gain popularity as a class of biomimetic polymers, the importance and demand for accurate force fields in molecular simulations also grow. Building on the vacuum-optimized Systematic and Extensible Force Field for Peptoids (STEPs) force field, here we present STEPs-SOL, a novel peptoid force field parametrization that effectively incorporates solvent effects to enhance the accuracy of peptoid simulations. The development of STEPs-SOL is based on the need for precise electrostatic modeling achieved through solvent-specific partial charge optimization. Our systematic approach significantly improves agreement with experimental measurements, reducing the mean absolute error in cis/trans ratio predictions (ΔGc/t) by an average of 38% across multiple peptoid residues and solvent environments. This improved parametrization addresses computational challenges associated with nonbonded energies while maintaining a workflow that relies on high-level quantum mechanical data rather than depending solely on limited experimental equilibrium properties. By evaluating the effects of conformational bias in restrained electrostatic potential (RESP) charge generation and examining their impact on peptoid conformations in various solvents, we enhance our understanding of peptoid structural dynamics while providing a more accurate modeling framework.