2025-09-19 東京科学大学
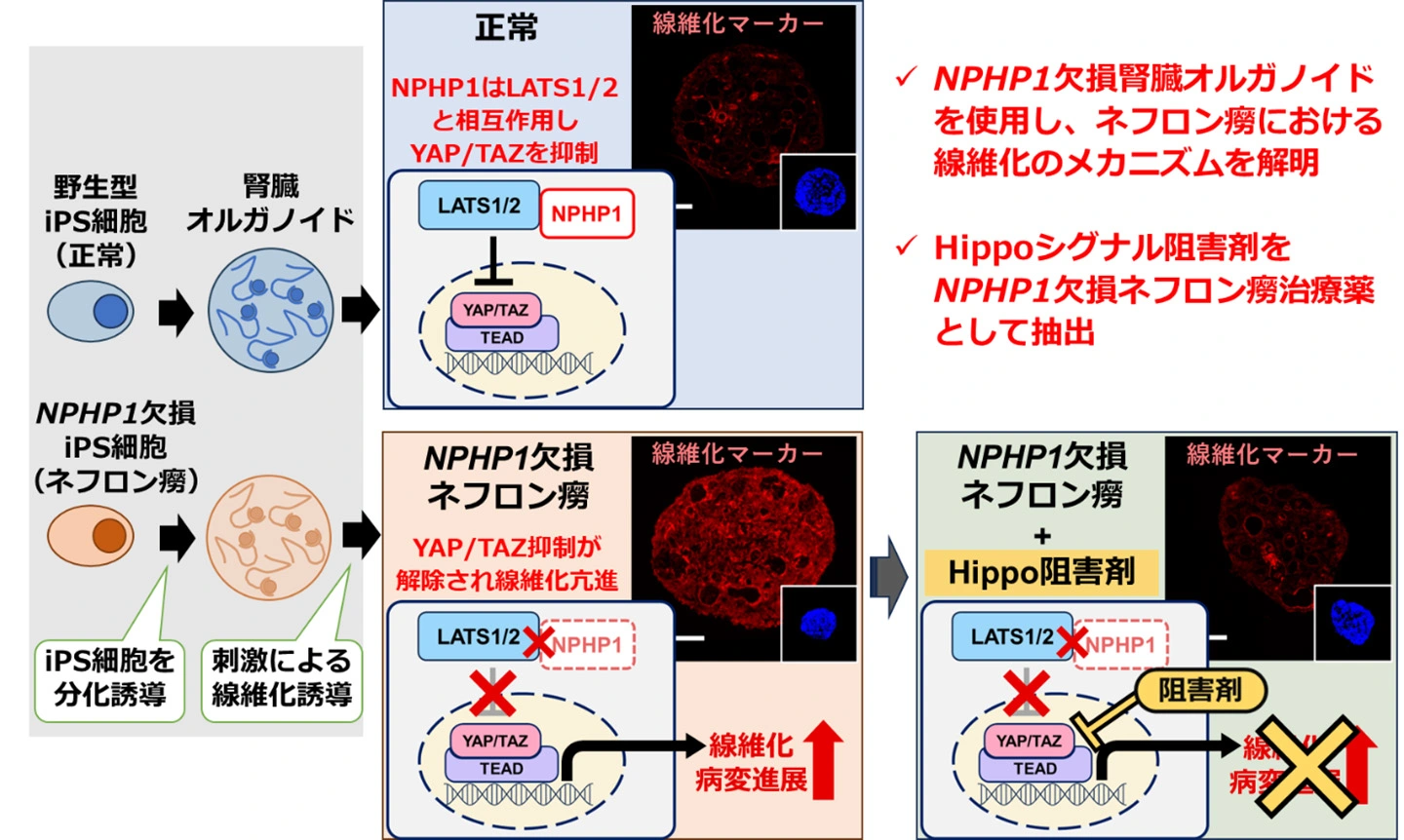 図.NPHP1欠損によるネフロン癆を再現したヒトiPS細胞由来腎臓オルガノイドモデルと、Hippoシグナル阻害剤の効果
図.NPHP1欠損によるネフロン癆を再現したヒトiPS細胞由来腎臓オルガノイドモデルと、Hippoシグナル阻害剤の効果
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/u0guhwdjs09t
- https://stemcellres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13287-025-04567-0
iPS細胞を用いた創薬研究により、NPHP1欠損性ネフロノフティシスの線維化における治療標的としてHippoシグナル伝達経路を同定 iPSC-based drug discovery identified the Hippo signaling pathway as a therapeutic target in the fibrosis of NPHP1-deficient nephronophthisis
Takefumi Suzuki,Koichiro Susa,Hiroaki Kikuchi,Yuta Nakano,Tomoki Yanagi,Yu Hara,Tamami Fujiki,Fumiaki Ando,Shintaro Mandai,Yutaro Mori,Takayasu Mori,Hiroaki Iwasa,Yutaka Hata,Shinichi Uchida & Eisei Sohara
Stem Cell Research & Therapy Published:19 September 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-025-04567-0
Abstract
Background
Nephronophthisis (NPH) is an autosomal recessive kidney disease, and NPHP1 is the most frequently affected gene. Tubulointerstitial fibrosis is the major phenotype of NPHP1-deficient NPH. The pathophysiology of NPHP1-deficient NPH is unclear because models representing the disease pathophysiology are lacking. Herein, we aimed to create a novel pathological model of NPH using 3D kidney organoids derived from human-induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and elucidated the pathophysiology while searching for therapeutic candidates.
Methods
NPHP1-deficient kidney organoids were generated from iPSCs. Fibrosis was induced by treatment with IL-1β. The effects of the Hippo signaling pathway inhibitors as therapeutic candidates were assessed. Fibrotic status was evaluated using immunofluorescence and quantitative PCR.
Results
NPHP1-/- kidney organoids were generated from iPSCs. Fibrosis induction with IL-1β considerably increased the expression of fibronectin and transcription of fibrosis-related genes in NPHP1-/- organoids. Long-term culture of NPHP1-/- organoids induced substantial fibrogenesis compared with wild-type organoids. Co-immunoprecipitation analysis revealed the binding of NPHP1 to LATS1/2—the main constituents of the Hippo pathway. IL-1β administration increased the expression of the key Hippo pathway genes in NPHP1-/- organoids. By contrast, the Hippo pathway inhibitors ameliorated IL-1β-induced fibrogenesis in NPHP1-/- organoids. Because one of the inhibitors, verteporfin, is in clinical use, its practical availability is expected from a drug-repositioning perspective.
Conclusions
Hippo signaling pathway is involved in the fibrotic changes associated with NPHP1-deficient NPH and the Hippo pathway inhibitors could be therapeutic agents.
Clinical trial number
Not applicable.


