2025-10-09 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/chem/202509/t20250911_1054417.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-025-01525-2
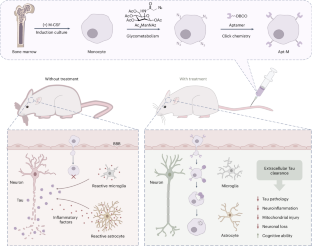
アプタマーを装備した単球を用いた細胞外タウの標的除去は、アルツハイマー病のマウスの神経炎症を軽減する Targeted clearance of extracellular Tau using aptamer-armed monocytes alleviates neuroinflammation in mice with Alzheimer’s disease
Yuting Zhuo,Yao Lu,Yan Zhu,Nachuan Wen,Guangjing Zou,Hongkun Lu,Xinyu Pei,Yutong Zhang,Qiang Zhang,Xin Wang,Wenjuan Zhang,Qingyang Zhang,Zhimin Wang,Sitao Xie,Chang-Qi Li,Weihong Tan & Liping Qiu
Nature Biomedical Engineering Published:01 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41551-025-01525-2
Abstract
Extracellular Tau determines the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, yet therapeutic strategies targeting it are hindered by poor brain delivery and limited clearance. Here we developed a Tau-clearing cell therapy based on monocytes functionalized with a high-affinity Tau-specific aptamer. The aptamer was covalently conjugated to the surface of monocytes (derived from bone marrow leucocytes and cultured under monocyte-inducing conditions) via bioorthogonal chemistry without affecting their viability or function. Upon intravenous administration in mice expressing mutant and disease-relevant human Tau, the engineered monocytes actively crossed the blood–brain barrier and accumulated in Tau-rich brain regions such as the hippocampus and striatum. They efficiently phagocytosed extracellular Tau, leading to a significant reduction in Tau burden. As a result, glial activation was suppressed, neuroinflammation was alleviated, and neuronal and mitochondrial integrity was preserved. Long-term treatment improved memory and spatial learning, without inducing toxicity or behavioural side effects. These results demonstrate that aptamer-guided monocytes can achieve targeted delivery, effective clearance and sustained neuroprotection, offering a promising strategy for therapeutic intervention in Alzheimer’s disease.