2025-10-21 ヒューストン大学(UH)
<関連情報>
- https://www.uh.edu/news-events/stories/2025/october/10212025-mohan-urinary-biomarkers-kidney-ln.php
- https://www.jci.org/articles/view/186143
尿タンパク質は、急性ループス腎炎と慢性ループス腎炎の根底にある異なる凝固および補体カスケードを明らかにする Urine proteins reveal distinct coagulation and complement cascades underlying acute versus chronic lupus nephritis
Ting Zhang, Jessica Castillo, Anto Sam Crosslee Louis Sam Titus, Kamala Vanarsa, Vedant Sharma, Sohan Kureti, Ramesh Saxena, and Chandra Mohan
The Journal of Clinical Investigation Published: October 1, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI186143
Abstract
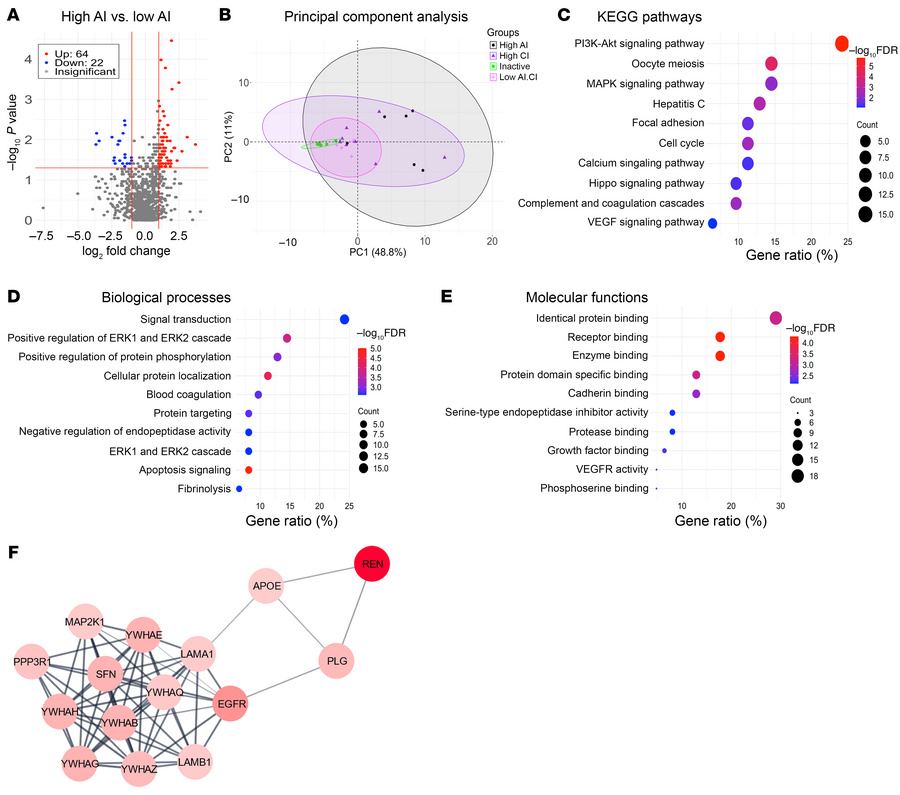
The current gold standard for assessing renal pathology in lupus nephritis (LN) is invasive and cannot be serially repeated. To assess if urine can serve as a liquid biopsy for underlying renal pathology, urine obtained from patients with LN at the time of renal biopsy were interrogated for 1,317 proteins, using an aptamer-based proteomic screen. Levels of 57 urine proteins were significantly elevated and correlated with pathology activity index (AI), notably endocapillary hypercellularity, fibrinoid necrosis, and cellular crescents. These included proteins pertaining to leukocyte/podocyte activation, neutrophil activation, endothelial activation, and markers of inflammation/anti-inflammation. In contrast, complement and coagulation cascade proteins, and proteins related to the extracellular matrix (ECM) emerged as the strongest urinary readouts of concurrent renal pathology chonicity index (CI), notably tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis. In vitro mechanistic studies revealed that complement proteins C3a and C5a increased the expression of profibrotic ECM proteins in macrophages and proximal tubule epithelial cells. Thus, carefully assembled panels of urinary proteins that are indicative of high renal pathology AI and/or CI may help monitor the status of renal pathology after therapy in patients with LN, in a noninvasive manner, without the need for repeat renal biopsies.