2025-10-24 基礎生物学研究所
Web要約 の発言:
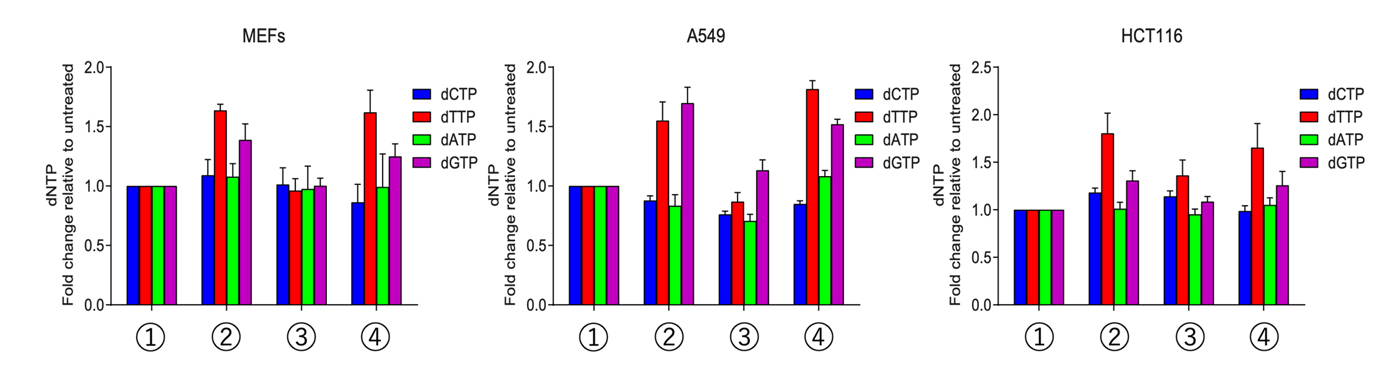
図1. ヌクレオシド補給時の細胞内dNTP量の変化
<関連情報>
- https://www.nibb.ac.jp/press/2025/10/24.html
- https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/53/19/gkaf1035/8285779
ヌクレオシド補充の解読:哺乳類の複製フォークの促進においてチミジンがリボヌクレオシドよりも優れている理由 Decoding nucleoside supplementation: how thymidine outperforms ribonucleosides in accelerating mammalian replication forks
Praveen Pandey, Kiminori Kurashima, Göran Bylund, Erik Johansson, Tomomi Tsubouchi, Andrei Chabes
Nucleic Acids Research Published:14 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaf1035
Abstract
Disruptions in deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) supply impair DNA replication and lead to genomic instability. While exogenous ribonucleosides (rNuc) have been suggested to alleviate replication stress by increasing dNTP levels, their precise metabolic effects remain unclear. Here, we show that rNuc supplementation primarily elevates CTP and UTP levels, with only modest increases in dCTP, and has minimal impact on replication fork speed across multiple mammalian cell lines. In contrast, thymidine (dThd), either alone or in combination with rNuc—as in EmbryoMax Nucleosides—significantly increases dTTP and dGTP levels, leading to accelerated replication fork progression. Notably, dThd, rather than rNuc, drives fork acceleration and counteracts fork slowdown caused by elevated dUTP, consistent with primer extension assays showing that dUTP transiently inhibits Pol ϵ-mediated DNA synthesis at template adenines. These results clarify the distinct roles of nucleosides in nucleotide metabolism, providing a mechanistic basis for how dThd promotes fork progression and preserves genomic stability.