2025-10-29 京都大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/ja/research-news/2025-10-29-0
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/sites/default/files/2025-10/2510_LiverInt_Okamoto_relj%20web-8a8d6d0ecbba27907950fce74357ef36.pdf
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/liv.70376
日本人集団における原発性硬化性胆管炎とHLA-C*07:02との関連 Association of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis With HLA-C*07:02 in a Japanese Population
Tatsuya Okamoto, Hideaki Okajima, Masashi Kadohisa, Miki Yamamoto, Elena Yukie Uebayashi, Shinya Okumura, Katsunori Sakamoto, Takashi Ito, Etsuro Hatano
Liver International Published: 23 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.70376
ABSTRACT
Background and Aims
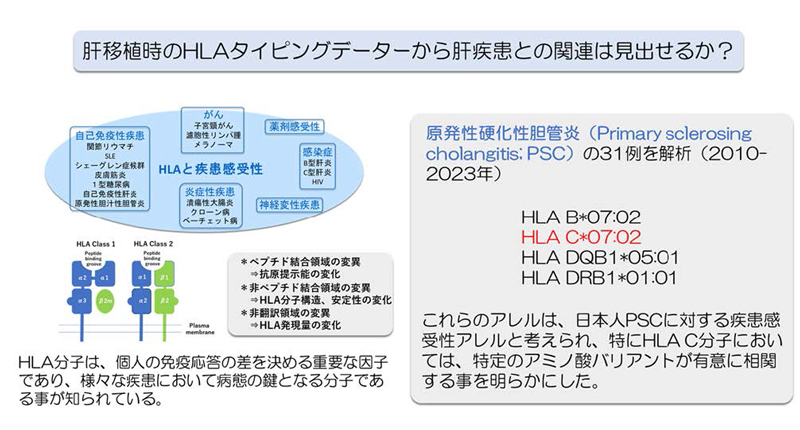
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a progressive, refractory liver disease often requiring liver transplantation (LT). The association between the disease onset and specific human leukocyte antigen (HLA) typing has been noted, but its relevance in the Japanese population is unknown.
Methods
The HLA 5 locus (HLA-A, B, C, DRB1 and DQB1) 4-digit genotyping results of 31 patients with progressive PSC who underwent LT at our institution were compared to those of 873 healthy Japanese controls.
Results
HLA-B*07:02 (p-corrected [pc] = 1.9 × 10-2), HLA-C*07:02 (pc = 3.9 × 10-5), HLA-DQB1*05:01 (pc = 3.7 × 10-2), and HLA-DRB1*01:01 (pc = 1.7 × 10-2) were identified as the susceptibility alleles for PSC. This correlation was stronger in patients with PSC complicated by ulcerative colitis than in those with PSC alone. Furthermore, analyses of the amino acid sequences of each HLA protein revealed that 15 amino acid residues of HLA-C were significantly associated with disease susceptibility (pc = 1.5 × 10-4-4.5 × 10-4).
Conclusions
HLA-C*07:02 is vulnerable to PSC aggravation in the Japanese population.
Summary
- HLA-C*07:02 allele was significantly associated with PSC in a Japanese population.
- The asociatin was more pronounced in cases in which PSC was complicated by UC.
- Amino acid variants of the HLA-C protein were responsible for the Japanese PSC.