2025-10-29 スウェーデン王立工科大学(KTH)
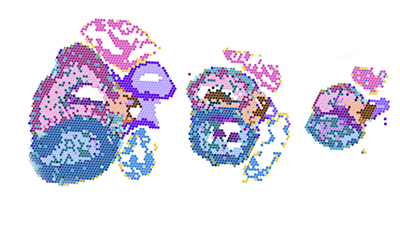
A visualization of molecular data generated from three distinct points in time during fetal heart formation.
<関連情報>
- https://www.kth.se/en/om/nyheter/centrala-nyheter/heart-blueprint-reveals-origins-of-defects-and-insights-into-fetal-development-1.1434488
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41588-025-02352-6
発達中のヒト心臓における時空間遺伝子発現と細胞動態 Spatiotemporal gene expression and cellular dynamics of the developing human heart
Enikő Lázár,Raphaël Mauron,Žaneta Andrusivová,Julia Foyer,Mengxiao He,Ludvig Larsson,Nick Shakari,Sergio Marco Salas,Christophe Avenel,Sanem Sariyar,Jan Niklas Hansen,Marco Vicari,Paulo Czarnewski,Emelie Braun,Xiaofei Li,Olaf Bergmann,Christer Sylvén,Emma Lundberg,Sten Linnarsson,Mats Nilsson,Erik Sundström,Igor Adameyko &Joakim Lundeberg
Nature Genetics Published:29 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-025-02352-6
Abstract
Heart development relies on topologically orchestrated cellular transitions and interactions, many of which remain poorly characterized in humans. Here, we combined unbiased spatial and single-cell transcriptomics with imaging-based validation across postconceptional weeks 5.5 to 14 to uncover the molecular landscape of human early cardiogenesis. We present a high-resolution transcriptomic map of the developing human heart, revealing the spatial arrangements of 31 coarse-grained and 72 fine-grained cell states organized into distinct functional niches. Our findings illuminate key insights into the formation of the cardiac pacemaker-conduction system, heart valves and atrial septum, and uncover unexpected diversity among cardiac mesenchymal cells. We also trace the emergence of autonomic innervation and provide the first spatial account of chromaffin cells in the fetal heart. Our study, supported by an open-access spatially centric interactive viewer, offers a unique resource to explore the cellular and molecular blueprint of human heart development, offering links to genetic causes of heart disease.